Texas is home to a wide variety of insects and bugs. The diverse climate of Texas, dry and hot in the west, and humid and wet in the eastern part, mean that insects like ants, beetles, chiggers, roaches and termites thrive. In addition, many bugs found in Texas include stink bugs, bed bugs, and Aphids may be a nuisance in the gardens and homes of residents. In addition insects that fly in Texas such as horseflies and mosquitoes, can cause painful bites and transmit disease.
The Lone Star State is teeming with intriguing creepy crawlies. Understanding how to identify Texas insects and bugs is essential to ensure that you are able to distinguish between beneficial insects and harmful ones. A good bug identification is also helpful in identifying ways to get rid of potentially dangerous insects.
Texas is renowned for its sprawling landscapes and diverse ecosystems, which makes it a sanctuary for an array of insects and bugs. From scorpions that lurk in the desert to fire ants sweeping across prairies, Texas bug and insect populations are essential to the ecosystem of the state.
This article will take you through this fascinating realm of Texas insects and bugs. Learn about their distinctive characteristics, how they can be found and what they do to the ecosystem.
Texas Bugs and Insects: A Quick Overview
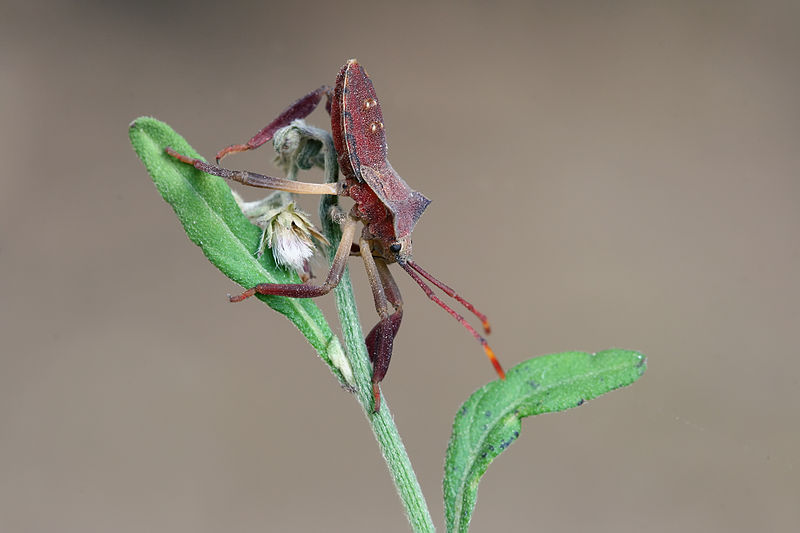

Image by and Credit to: Muhammad Mahdi Karim
In Texas there is a tendency for people to refer to the term “bugs” to refer to insects that are annoying. However, only insects that belong to the family of Hemiptera are categorized as genuine bugs. They are recognized by sucking and piercing the mouthparts (proboscis) they utilize to sucking plant sap. Like all insects, bugs come with six legs.
However the insect class (Insecta) is larger than the bug order (Hemiptera). Insects are distinguished by their antennae dimensions, their six legs as well as their wing structure and distinct marks. Thus, all bugs are classified as insect species; however they are not all insects in the scientific sense.
This article will help you identify different kinds of Texas bugs and insects. This article covers all kinds of arthropods, annoying insects and arachnids that are considered bugs, regardless of whether they are genuine bugs or not.
List of Different Types of Texas Bugs (with Pictures!)
Let’s take a closer look at some of the commonly seen Texas bugs that you can expect to see in your house or backyard.
Kissing Bugs (Triatoma gerstaeckeri)
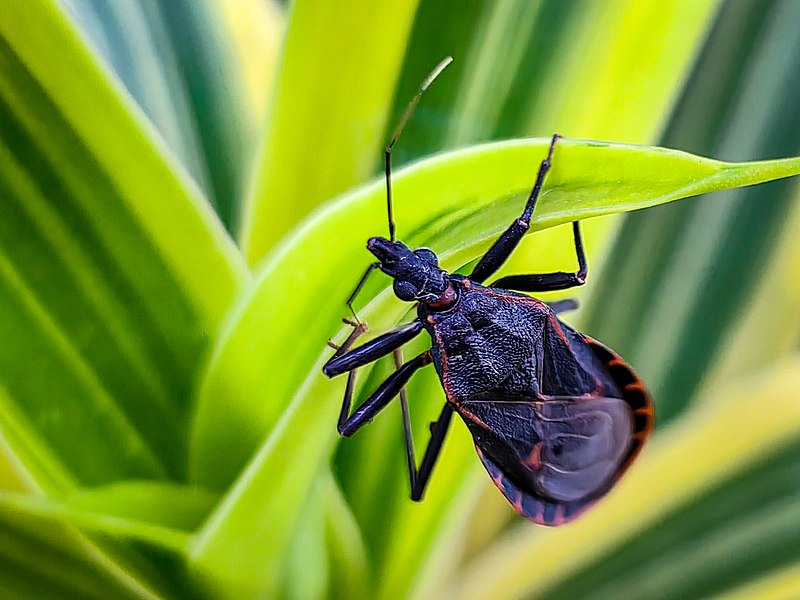

Image by and Credit to: Heigen Villacarlos
Kissing bugs are blood sucking Texas insects sporting blackish brown bodies, and orange or yellow marks on their wings (elytra). The tiny disease-carrying insects have an oval-shaped shape and a thin proboscis, which they utilize to eat blood. Adult kissing bugs are 0.79″ to 1.18″ (20 to 30 millimeters) in length.
Kissing bugs are believed to carry the parasite called Trypanosoma cruzi that causes Chagas disease. It is essential to stop insects from infiltrating your home by sealing gaps around windows and doors and by installing insect screens.
The CDC advises against kissing or squashing bugs. Instead, put the bug inside a container and then take it to a health center or local extension office.
How to Identify: Kissing bugs are recognized by their oval, brown bodies that have yellow or orange stripes along the edges of their abdomens.
Aphids (Aphidoidea)
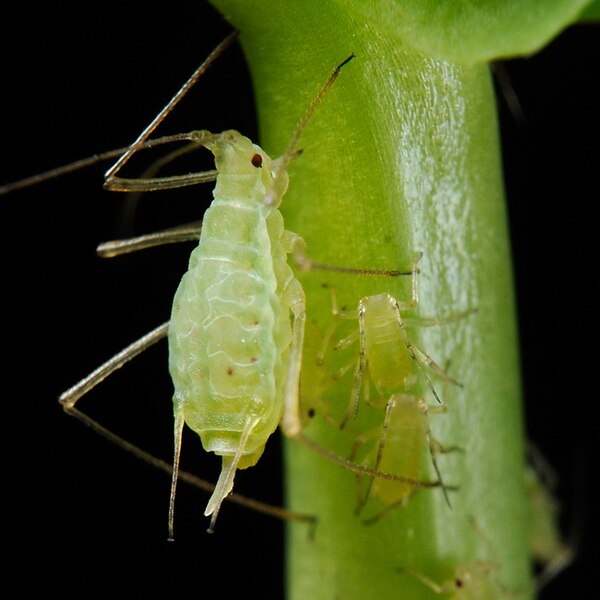

Image by and Credit to: Shipher Wu
Aphids are a common insect found in Texas with a size of 0.12 inches (3 millimeters) long. Aphids are a frightful insect that feeds on plants, greenhouse crops and houseplants in Texas. The tiny insects can be identified by their pear-shaped bodies, their six legs, and antennae that are long. Aphids are genuine bugs that are usually seen in a variety of shades, such as red, green, yellow or black.
Woolly aphids are a different kind of sap-sucking insect that destroys plants. These tiny insects are easy to recognize due to their white fuzzy appearance.
Woolly Aphids infestation
Aphids can be a nuisance in gardens, greenhouses, as well as homes because they reproduce rapidly and are able to infest plants in huge quantities. Aphids bite stems, leaves, and flowers, causing damage to the health of the plant. They also harm plants through the release of the sticky substance honeydew, which encourages the growth of mold.
How to Identify: Aphids are tiny insects that range from 0.08″ to 0.12″ (2 – 3 millimeters) in length. They can be identified through their pear-shaped bodies, soft body and soft shape. Aphids are usually located in clumps on the leaves’ undersides.
Giant Water Bugs (Belostomatidae)
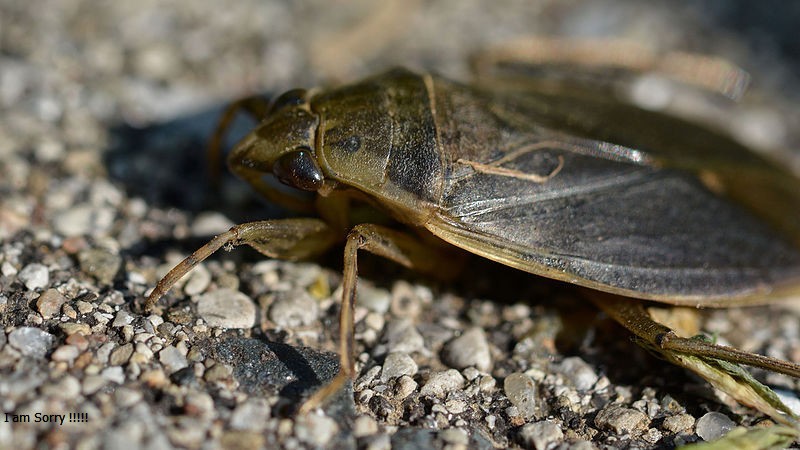

Image by and Credit to: Ryan Hodnett
Giant Water Bugs are huge insects that have an oval shape and flattened brown bodies as well as a total length of around 2 inches (50 millimeters). One distinctive characteristic of these huge aquatic bugs is their massive front legs that they employ to catch and secure their prey. Their hind legs, however, are mostly employed for swimming in the water.
Giant water bugs can also be identified under the names Texas toe-biters as well as alligator ticks and electric-light bugs. In Florida the big bugs are known as alligator fleas. The common names for them suggest that the big bugs utilize their pincers for painful bites if they are threatened. However, they aren’t harmful to humans.
How to Identify: To find the giant Texas bug populations, search for their size and dark and black colors, oval-shaped flat shape as well as long, slender legs. It is common to find bugs in ponds, streams along with other natural habitats that are fresh water.
Dog-Day Cicada (Neotibicen canicularis)
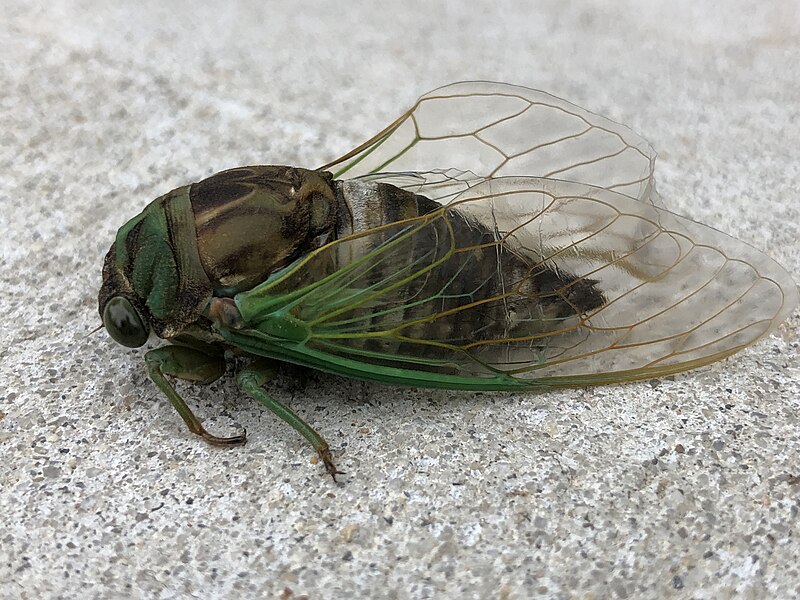

Image by and Credit to: Famartin
The dog-day cicada can be described as a big dark bug, distinguished through its bulging, green eyes and the mottled patterns that are visible across its rear. The common Texas bug is green, brown, black and white markings on its body. It also has transparent wings and strong legs that are large and sturdy and measures 1.06″ to 1.30″ (27 mm to 33 millimeters) in length.
The dog-day cicada are its distinct mating calls. While flying, it produces an extremely high-pitched whining sound similar to the sound of a saw that is cutting through wood. It’s most active on hot and hot summer days.
How to Identify: The dog-day cicada has a dark-bodied insect that has huge wings, dark brown or green markings.
Southern Green Stink Bug (Nezara viridula)
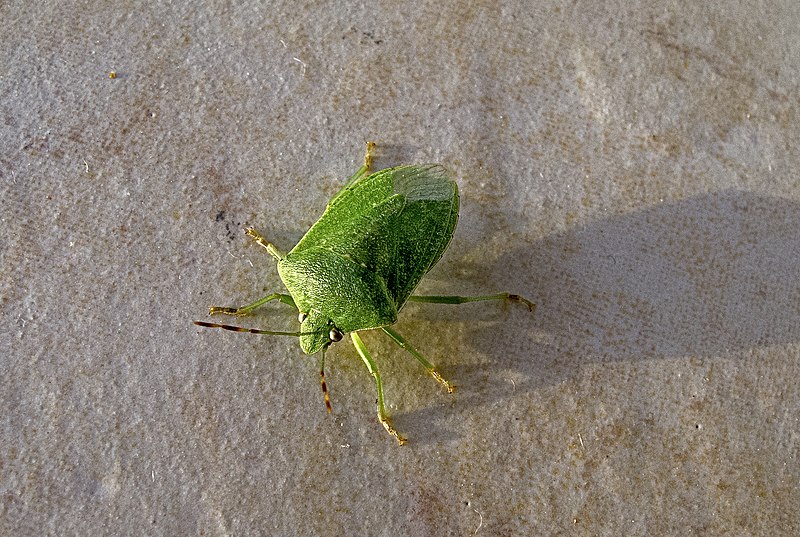

Image by and Credit to: Katya
Southern green stink bugs are tiny bright green insects that have an elongated body. It is commonly found in backyards in Texas The bug has an unusual triangular form and is 0.48″ (12 millimeters) in length. The green bug is characterized by six legs, eyes that are reddish and long antennae that are tan-brown in color.
“The green stink bug” takes its name because of the unpleasant smell it emits when the bug is threatened or smashed.
This southern-facing bug experiences many color variations during its stages of growth (instars). It may be black, with rows of creamy white spots, or have an orange back, or become dark brown during winter. In addition, stink bugs can damage crops.
The green bugs are thought to be agricultural pests because they feed on a variety of plants, such as vegetables, fruits, and grains. They make use of their proboscis to penetrate plant tissue and then suck out juices, causing destruction to plants.
Other stink bug species found in Texas are:
Spined Soldier Stink Bug (Podisus maculiventris):
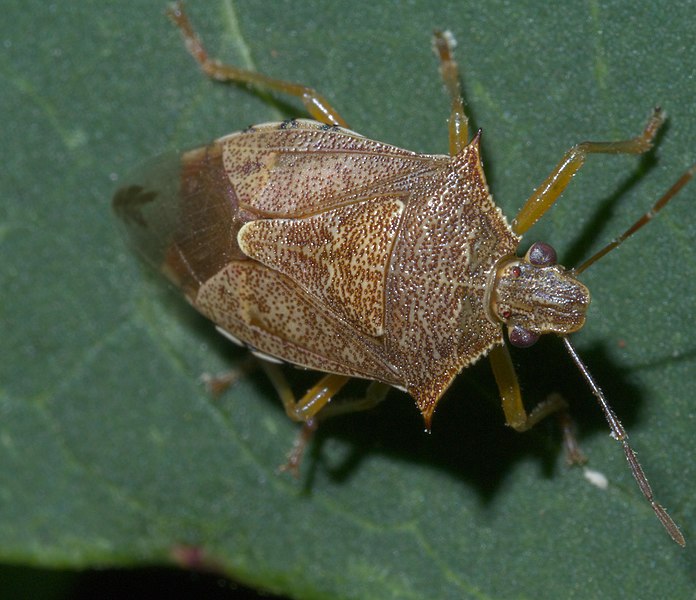

Image by and Credit to: xpda
The Spined Soldier stink bug, scientifically named Podisus maculiventris, plays a beneficial role in agriculture as a natural predator of various harmful insects. With their spined appearance, these bugs are effective hunters, preying on pests like caterpillars and aphids. Farmers often encourage the presence of Spined Soldier stink bugs in their fields as a natural pest control method, reducing the need for chemical insecticides and promoting eco-friendly farming practices.
How to Identify: To locate stink bugs in the Texas landscape, look out for their distinctive shield-shaped body as well as distinctive triangular patterns across their bodies.
Rice Stink Bug (Oebalus pugnax):
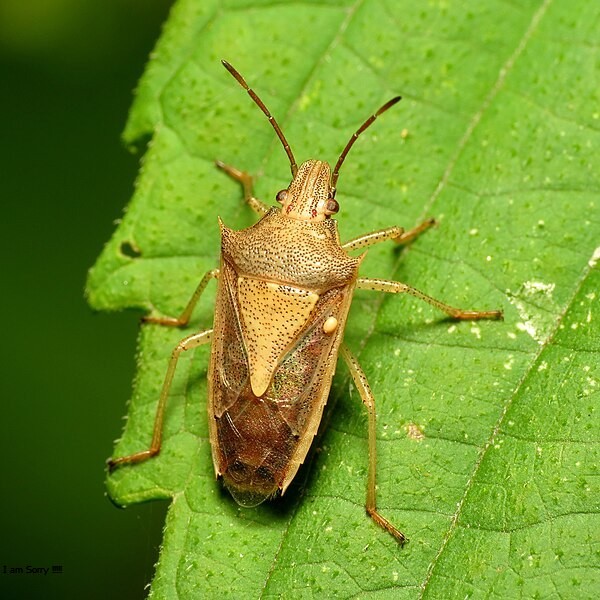

Image by and Credit to: Katja Schulz
Oebalus pugnax, commonly known as the Rice stink bug, is a major concern for rice farmers worldwide. These insects feed on developing rice grains, leading to yield losses and economic setbacks. Rice stink bugs are challenging to control due to their mobility and adaptability to various environmental conditions. Farmers need to monitor their fields closely and employ targeted pest control methods to safeguard their rice crops from these destructive bugs.
Conchuela Stink Bug (Chlorochroa ligata):
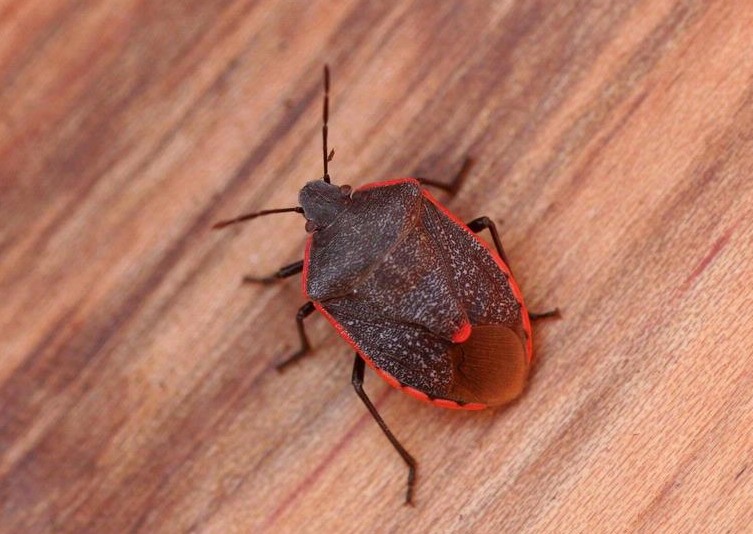

Image by and Credit to: Whitney Cranshaw
The Conchuela stink bug, Chlorochroa ligata, is a common agricultural pest that poses a significant threat to various crops. These stink bugs feed on plant juices, causing wilting, discoloration, and reduced harvest yields. Farmers often face challenges in controlling Conchuela stink bugs due to their rapid reproduction and resilience. Implementing integrated pest management practices is crucial to minimize the damage caused by these pests and ensure healthy crop production.
Harlequin Bug (Murgantia histrionica):
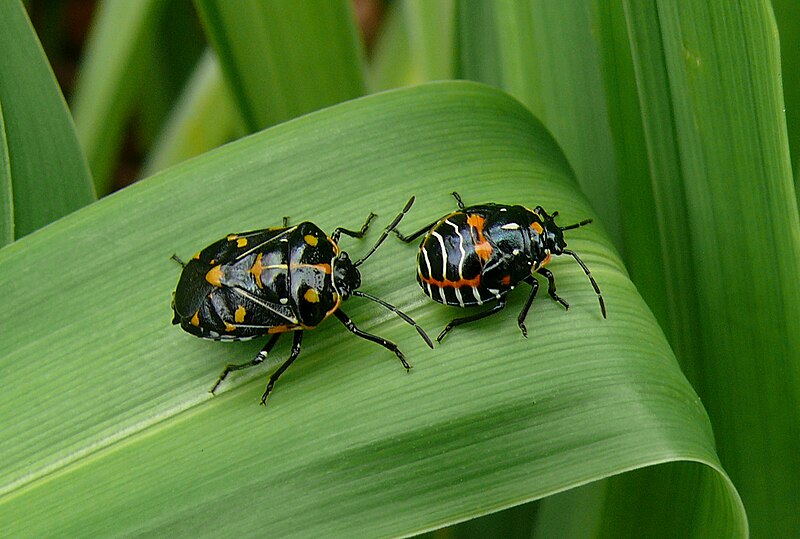

Image by and Credit to: Linda Tanner
The Harlequin bug, scientifically known as Murgantia histrionica, is a notorious agricultural pest known for its vibrant colors and destructive nature. These insects target a variety of crops, including cabbage, kale, and mustard greens. Harlequin bugs damage plants by piercing them and sucking out their juices, leading to wilting and reduced yield. Effective pest management strategies are essential to protect crops from the economic impact of Harlequin bug infestations.
Bed Bugs (Cimex)
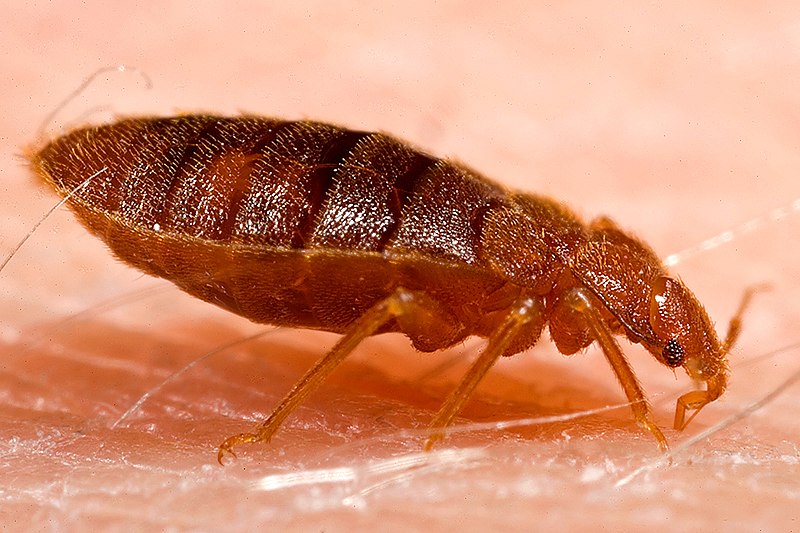

Image by and Credit to: Piotr Naskrecki
Bed bugs are small oval-shaped blood sucking insects which are reddish-brown. Bed bugs are around the size of a seed from an apple with a size of 0.19″ to 0.27″ (5 to 9 mm). These tiny, wingless insects are armed with six legs, piercing sucking mouthparts to eat the blood of their victims, and six legs and a red-colored color after eating.
Bed bugs are often found in the cracks of mattresses, beds, and furniture. They are active during the night and feed on blood of both animals and humans. The most obvious symptoms of bed bugs are the bloody marks they leave behind. Because these tiny creatures are so tiny it is difficult to eradicate without expert pest control.
Other indicators of bed bug infestation include a sour, musty smell, dark reddish-brown-black like stains of pepper (feces) and bodies that have molted.
How to Identify: Bed bugs are tiny, reddish-brown flies with flat, oval-shaped bodies and a length of 0.19″ (5 millimeters) in length.
List of Different Types of Texas Insects(with Pictures!)
Let’s examine in depth the most common Texas insects that a lot of people refer to as pesky bugs.
Termites (Isoptera)
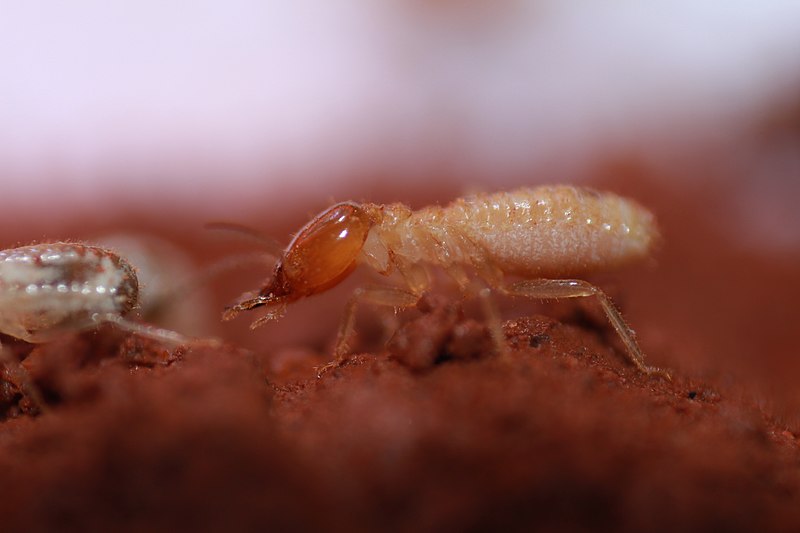

Image by and Credit to: Nikhil More
Termites are tiny and destructive insects that are found in colonies and eat wood. These tiny, ant-like insects are slender and soft with a body that measures 0.37″ (9.5 millimeters) long. They are distinguished with their straight, elongated antennae, a thick waist, and straight beads-like segments around their abdomens.
Termite pests that are found in Texas may be subterranean bugs (Rhinotermitidae) as well as dry wood termites (Kalotermitidae).
Subterranean termites build nests in the ground that cause the most destruction. They could cause irreparable damage to wood structures since they consume wood or paper as well as other plants. They are found all over Texas.
Dry-wood termites are usually found in coastal regions of Texas and up to San Antonio. Similar to their subterranean counterparts, dry wood termites could cause a lot of destruction on wooden buildings.
Jamaican Field Cricket (Gryllus assimilis)
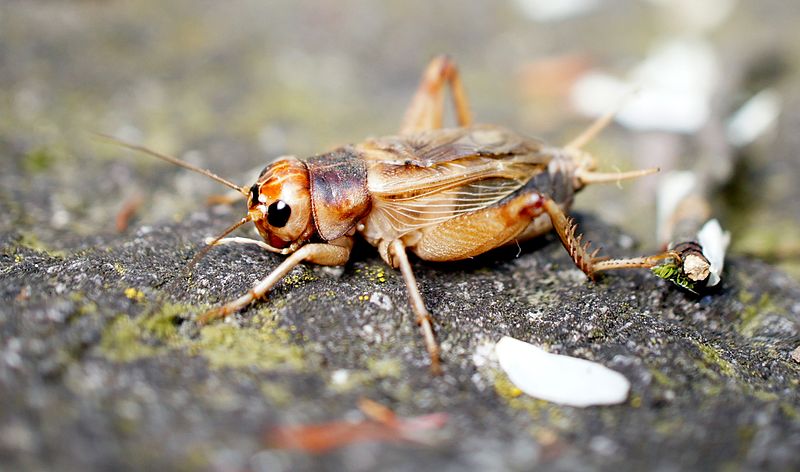

Image by and Credit to: Schönitzer
A black cricket is a typical insect found in gardens of southern Texas. It can be identified by its reddish-brown and dark brown coloring, its rounded head with black eyes and its large size that can reach 1″ (25 millimeters) in length. Male crickets make noises of chirping.
Jamaican field crickets may become an issue when massive outbreaks are observed during September and August. Dead crickets in large quantities are often found on sidewalks and appear unsightly and emit foul smells. Sometimes, they be a nuisance in indoor areas. They could harm clothing, drapes, or even walls by releasing their urine.
How to Identify: Jamaican field cricket found in the southern parts in the Lone Star State and is distinguished by its dark color with long antennae and the prominent hind legs.
Silverfish (Lespisma saccahrina)
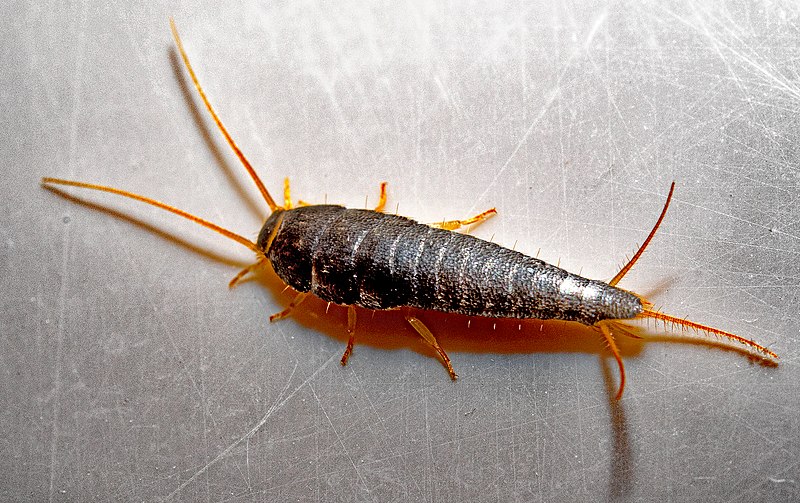

Image by and Credit to: Géry PARENT
Silverfish is a tiny insect that is wingless and has an extended body covered with silvery-gray scales. Silverfish measures 0.5″ to 1″ (13 – 25) in length. It is identified by the three slim appendages near its tail as well as two long antennae on the body’s front. The bug is shiny skin and appears scaly. It is able to slither through the floor.
Silverfish can be located in damp areas like kitchens, bathrooms and basements. The name comes due to its vivid color and fish-like movements when it runs in order to stay clear of light, and seek dark spots. The pests are harmless but they can be insects due to their capability to destroy paper products or clothing items, and also cause food poisoning.
How to Identify: Silverfish is identified by its shaped carrot body, encased with silver-gray scales. It also has two long antennae, as well as three tail-like appendages to the rear. The speedy and wriggling movements make it easy to recognize.
Earwigs (Dermaptera)
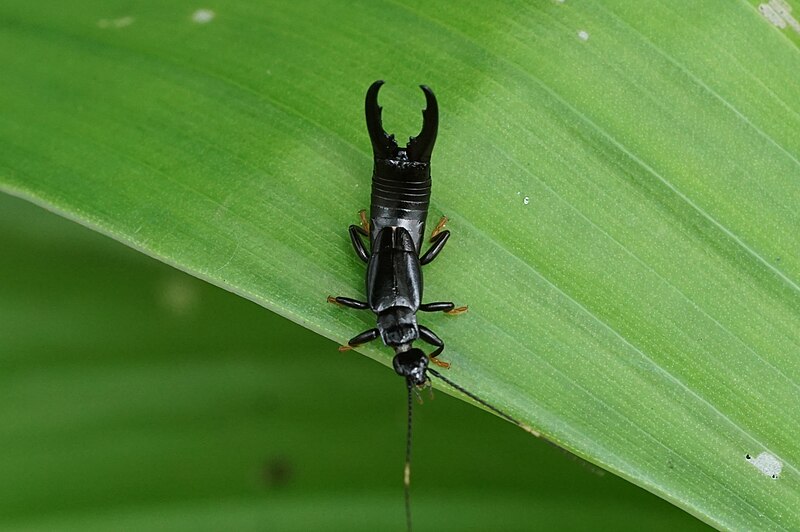

Image by and Credit to: Vengolis
Earwigs are tiny black elongated insects with distinct forcep-like appendages on the bottom of their abdomens. The slender bugs can be identified by their dark, flattened body with tail pincers as well as long segments of antennae. These insects can be located in moist areas like under logs, rocks, or in garden mulch.
Earwigs are 1″ (25 millimeters) long and grow during the night. In the daytime they remain in dark locations. In the evening they feed on insects, such as aphids and mites. In the indoors, they hunt for sweet, oily and oily food items. Earwigs can be nuisance pests, but are not harmful to humans.
How to Identify: Earwigs are easily identified bugs with long body, cerci that resemble pincers and membranous wings that are folded under their short, supple forewings.
Cigarette Beetles (Lasioderma serricorne)
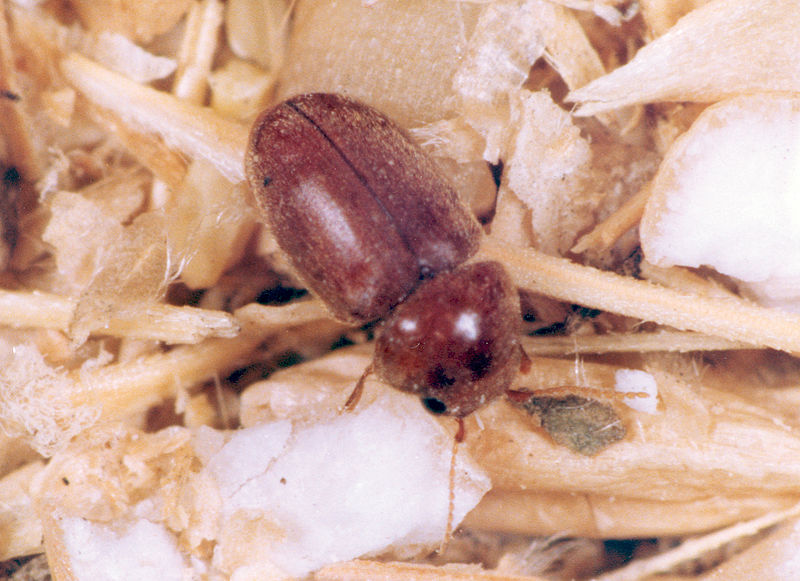

Image by and Credit to: CSIRO
Cigarette beetles are recognized as tiny brown insects sporting an oval bodies that are covered in fine hairs, with a distinctive form with a humpbacked shaped shape, and antennae that are clubbed. The brown beetles are 0.08″ to 0.11″ (2-3 mm) in length. They look like beetles from a drugstore and the pesky insects mostly are found in tobacco plants.
Drugstore beetles and cigar beetles can also be a problem for pantry pests in Texas in the event that they are introduced into the cabinets. The tiny bugs consume stored cereals as well as dried fruit grains, spices and even flour.
How to Identify: When trying to identify cigarette beetles, search for their reddish-brown color, their humpbacked form and clubbed antennae.
Carpet Beetles (Anthrenus and Attagenus)
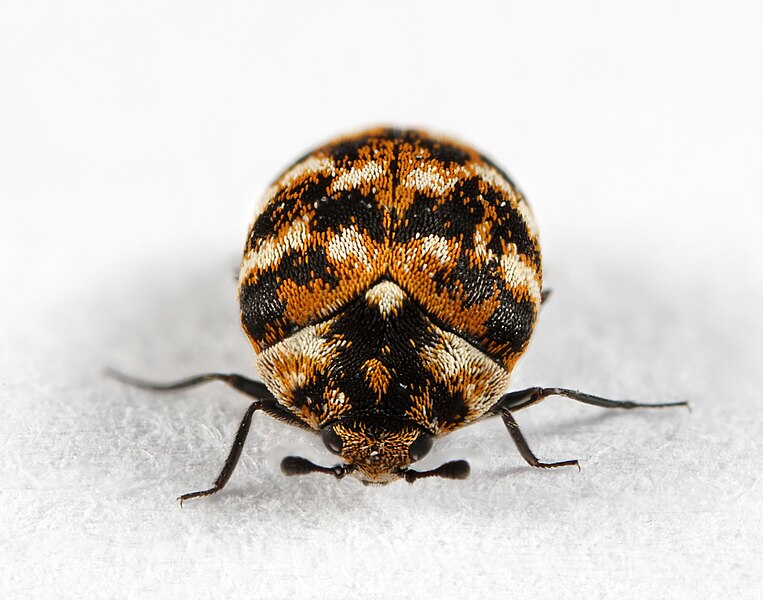

Image by and Credit to: AJC1
Carpet beetles are tiny, oval-shaped insects that are common in houses in Texas. Adult beetles are in the range of 0.06″ and 1.25″ (1.5 to 3 millimeters). They’re usually either dark gray or, with scattered white, brown as well as black designs on their elytra. Carpet beetles are a swarm of bugs during their larvae stage as they eat carpets, clothing and other household objects.
The larvae of carpet beetles are tiny hairy worms frequently referred to as “woolly bears.” They vary in hues ranging from brown to white and are covered with bristle-like hairs. The larvae feed on natural fibers including silk, wool and fur, in addition to insect carcasses and feathers. If they are not treated they can cause severe destruction to upholstery, carpets and even clothing.
Here are the most notorious types of carpet beetles that are found in houses in Texas and their distinctive characteristics:
Furniture Carpet Beetle (Anthrenus flavipes):
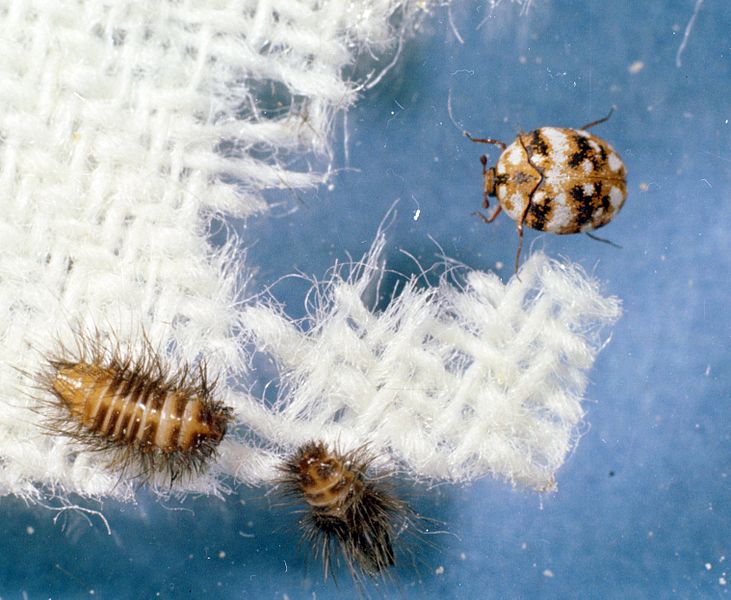

Image by and Credit to: Clemson University
Furniture carpet beetles, scientifically named Anthrenus flavipes, are destructive pests that target various household items, including furniture, textiles, and carpets. Their larvae feed on natural fibers, causing irreparable damage and unsightly holes. Regular inspection of furniture, carpets, and stored items is essential to detect early signs of infestation. Prompt action, such as cleaning, vacuuming, and utilizing insecticides, can help eradicate furniture carpet beetles and prevent further harm to household items.
Common Carpet Beetle (Anthrenus scrophulariae):
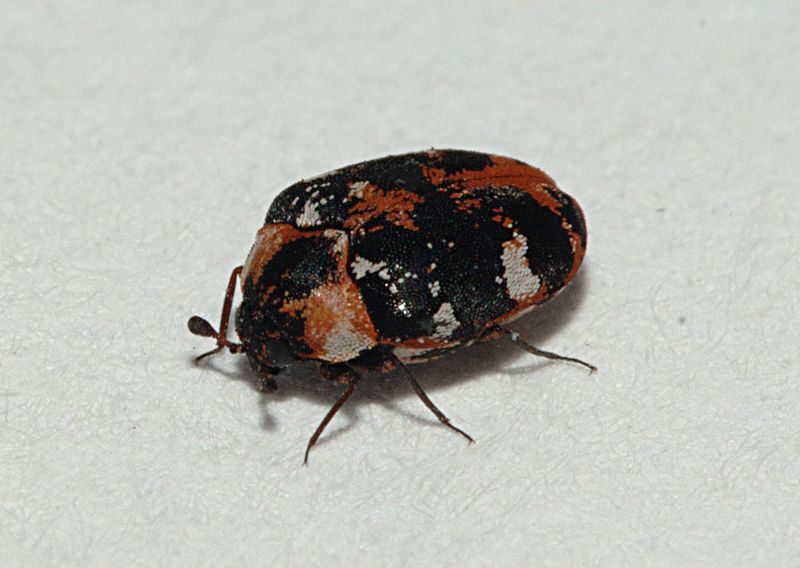

Image by and Credit to: Kurt Kulac
The common carpet beetle, Anthrenus scrophulariae, is a household pest known for its voracious appetite for natural fibers, including wool, silk, and feathers. These tiny insects and their larvae can wreak havoc on carpets, clothing, and upholstery if left unchecked. Preventive measures like frequent cleaning, proper storage, and sealing entry points into homes are crucial to safeguarding against common carpet beetle infestations and preserving household belongings.
Varieties of Carpet Beetle (Anthrenus verbasci):
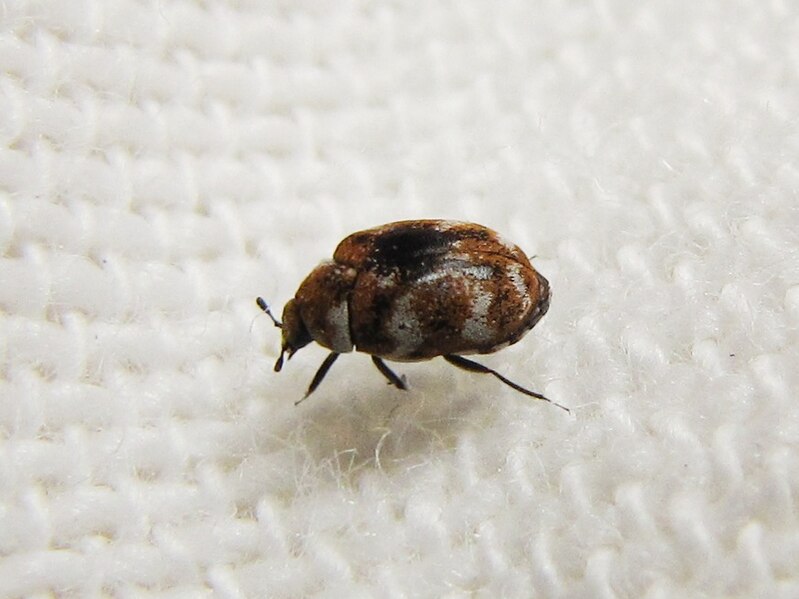

Image by and Credit to: Toffel
Varieties of carpet beetles, specifically Anthrenus verbasci, are small insects notorious for infesting homes and damaging fabrics, carpets, and stored products. These beetles and their larvae feed on natural fibers, fur, and even stored food items, causing significant damage. Effective pest control measures, such as regular cleaning, vacuuming, and proper storage, are essential to prevent infestations and protect valuable items from these destructive pests.
Chiggers (Trombiculidae)
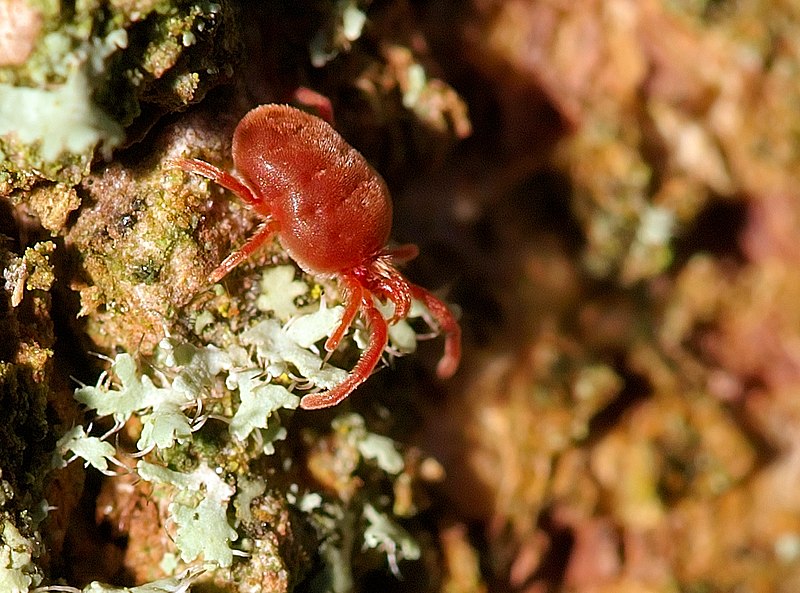

Image by and Credit to: Luc Viatour
Chiggers are tiny red mites that are not even apparent to the untrained eye. Chiggers aren’t actually insects, rather, they’re an arachnid species that has a red color. They are 0.01″ (0.4 millimeters) and feature a round body with eight legs. They are renowned for feeding on skin and biting it, leaving bruises that are red.
Chiggers are in full force during the hot and humid seasons in Texas. They cause pain by puncturing the skin with their sharp jaw parts infusing an enzyme which causes skin to break down. This causes red rash swelling, as well as secondary skin infections due to scratching.
Chiggers are two of the most gruesome species in Texas are as follows:
Eutrombicula splendens
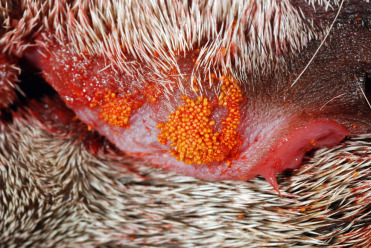
Image by and Credit to: sciencedirect.com
Eutrombicula splendens, another species of chigger mites, is prevalent in warm and humid regions. These mites, similar to their counterparts, cause itching and skin irritation upon contact. They are commonly found in grasslands and wooded areas. Protecting yourself by wearing long-sleeved clothing and applying insect repellents can help minimize the risk of Eutrombicula splendens bites.
Being aware of the habitats and behaviors of these chigger species is crucial for individuals venturing into their natural environments, ensuring a more comfortable and itch-free experience.
How to Identify: Chiggers are small and are difficult to detect by your naked eyes. The best method of identifying Chiggers is to look for the skin rash and red welts they “bites” cause.
Common Chigger (Trombicula alfreddugesi)
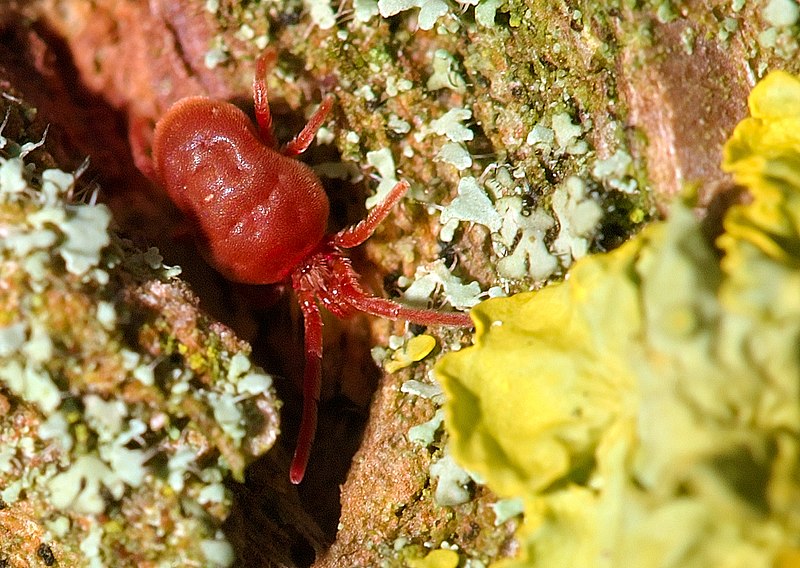

Image by and Credit to: Luc Viatour
The common chigger, scientifically known as Trombicula alfreddugesi, is a tiny mite notorious for causing intense itching and discomfort. Found in grassy areas and forests, these minuscule insects attach themselves to human and animal skin, causing itchy, red welts. Chigger bites can lead to skin irritation and allergic reactions. Understanding their habitats and taking preventive measures, such as wearing protective clothing, is essential to avoid chigger bites during outdoor activities.
Fleas (Siphonaptera)
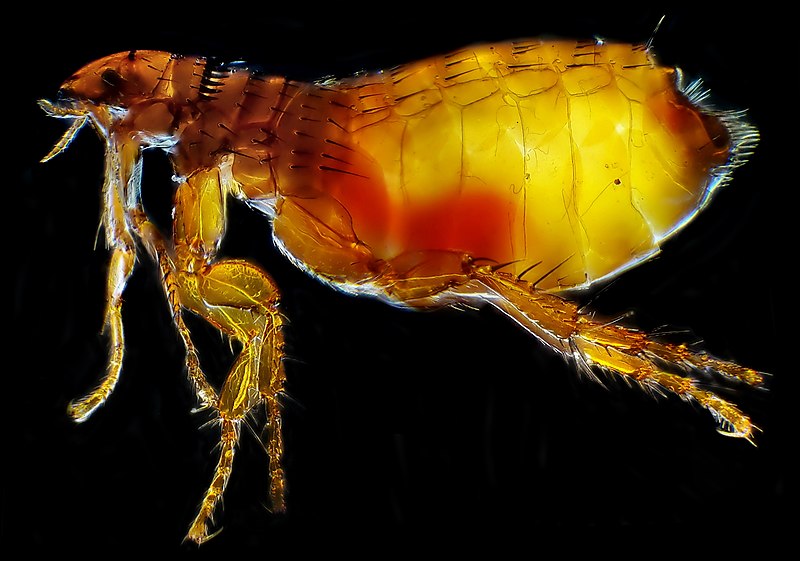

Image by and Credit to: Andrei Savitsky
Fleas are tiny parasites with no wings that are blood-feeding and can leap over across long distances. They are usually dark brown or black with a pear-shaped, flattened body and hind legs that are long to jump. But, these tiny bugs are so tiny you will require a microscope to discern their distinct traits.
Tiny fleas can grow to 0.12″ (3 millimeters) in length. In addition to being fantastic jumpers they can swiftly move through hair or fur. Bug bites can trigger itchy red bumps to the skin. In addition, bites from fleas can transmit worms and bacterial diseases.
In Texas the fleas are a frequent issue because of the warm temperatures and the abundance of animals. It is essential to implement preventative steps for example, frequently treating your pet for the presence of fleas, and maintaining clean outdoor areas to minimize the chance of getting infested.
How to Identify: Fleas can be identified through their black or dark brown color, their tiny pear-shaped body with a flattened shape, and their long hind legs to aid in jumping.
Fire Ants (Solenopsis)
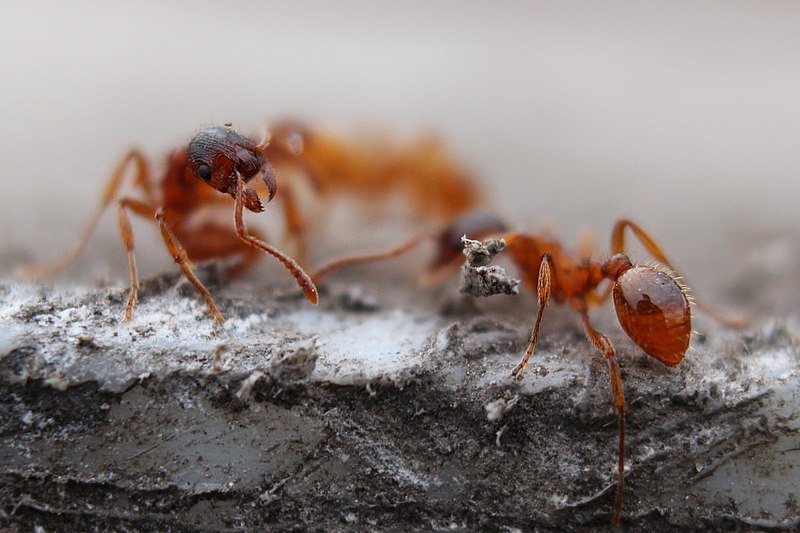

Image by and Credit to: Magdalena Smyczek
Fire ants are tiny, reddish-brown stinging insects known for their aggressive nature of their behavior and the painful stings. The tiny, pesky insects can be distinguished by a round head and abdomen, as well as a slim waist that is divided into two segments. They typically range from 0.09″ to 0.23″ (2.24 – 6 mm) and are located throughout the south of the United States, including Texas.
Fire ants form huge mounds that can be an issue in gardens or parks as well as agricultural zones. They sting people by piercing into skin and injecting poisonous venom through their stingers. The stings of fire ants are extremely painful and can cause extreme swelling, nausea and vomiting.
How to Identify: The fire insects are distinguished by their reddish-brown to black red coloration, a segment of the body, with a two-segmented waist and painful stings if you provoke them.
Tawny Crazy Ant (Nylanderia fulva)
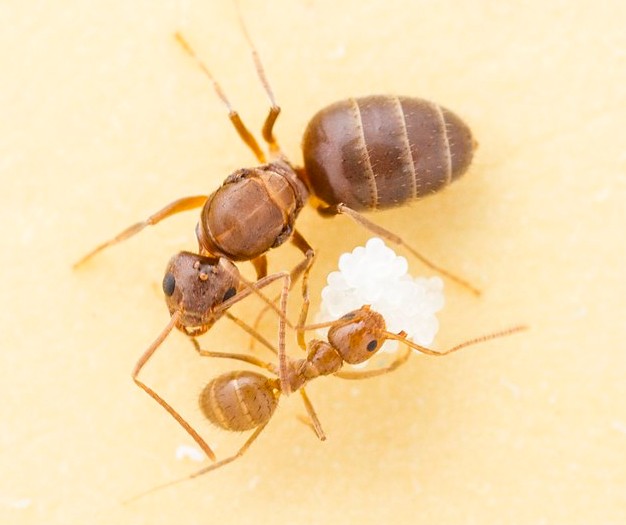

Image by and Credit to: Insects Unlocked
The tawny wild an ant is a small species of invasive reddish brown that is able to fly. Also known as “the raspberry crazy ant” these pesky insects can be identified by their slim bodies as well as their long, slim legs and a bulbous abdomen. The ants’ brownish-pale skins grow 0.12″ (3 millimeters) in length. They are named after their fast and unpredictable moves, which are deemed “crazy.”
Tawny ants attack and then release formic acid in a defensive mechanism. They are able to quickly spread and infest areas, which makes your time in the affected areas difficult. They are also attracted by electrical devices and eat through wires, causing short circuits.
How to Identify: The distinguishing characteristics of the tawny ant include its small size of 0.12″ (3 millimeters) long, its reddish-brown color and rapid, erratic motions as it searches in search of food.
Palmetto Bug (Eurycotis floridana)
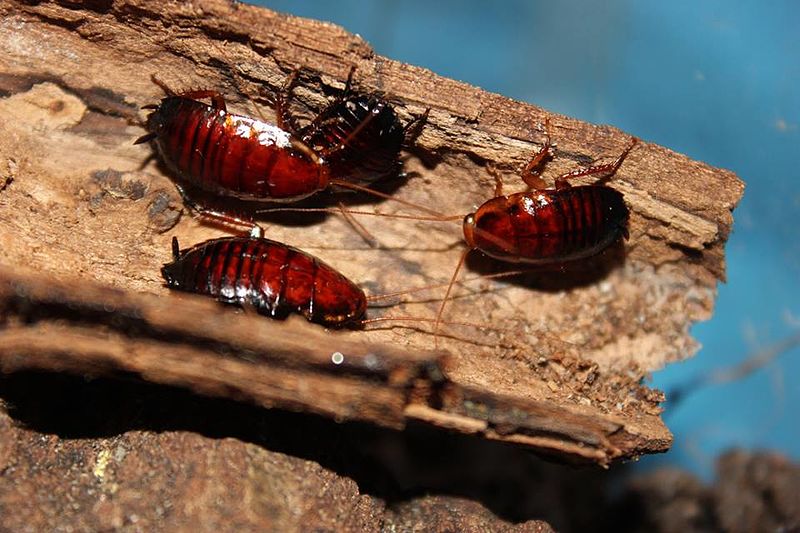

Image by and Credit to: Happy1892
The palmetto bug is recognized as a huge, reddish-brown insect that is commonly found in Texas. It is also known as”the Florida wood cockroach distinguishing characteristics of this bug include its forewings that are short, and the size of as much as 1.6″ (40 millimeters) long, and the capability to fly. Dark brown bugs are frequently attracted by humid, warm environments.
In contrast to other roaches that carry diseases Palmetto bugs aren’t an important pest in the indoor environment. The roaches with a dark brown and glossy appearance prefer to reside out within Texas landscapes. It can be found under leaves, in the bushes, or in cracks. It can sometimes make its way into bathrooms and homes in warmer parts of Texas.
How to Identify: The palmetto insect is a large reddish-brown, or blackish-brown cockroach that has a shiny oval-shaped body, long antennae as well as six legs. It is usually located in humid and warm regions.
Cockroaches (Blattaria)
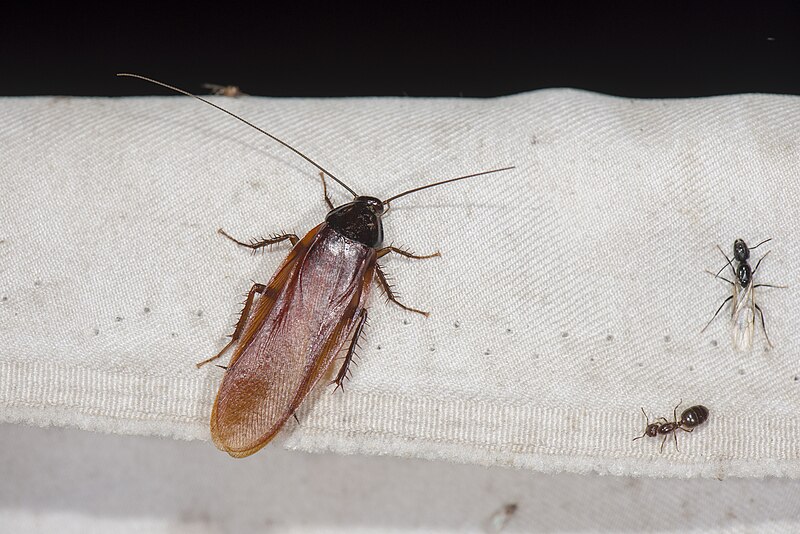

Image by and Credit to: LiCheng Shih
German Roach (Blattella germanica) on the left, and American the roach (Periplaneta Americana) left
Cockroaches are insects characterized by their reddish brown and dark brown flattened bodies with long antennae and quick motions. They are often referred to as roaches. Cockroaches from Texas are 0.43″ to 1.6″ (11 to 40 millimeters) in length (11-40 mm). These gruesome bugs are usually found in dark crevices and caves, infesting houses and spreading disease.
The dry, hot, and often humid climate in Texas makes it possible for roaches to be a nuisance within homes. The brown bugs look for dark, moist areas close to food sources to be fed and multiply. Certain cockroaches found in Texas may also fly.
Here are descriptions and characteristics of three frequent species of roach bugs in Texas:
Oriental Cockroach (Blatta orientalis)
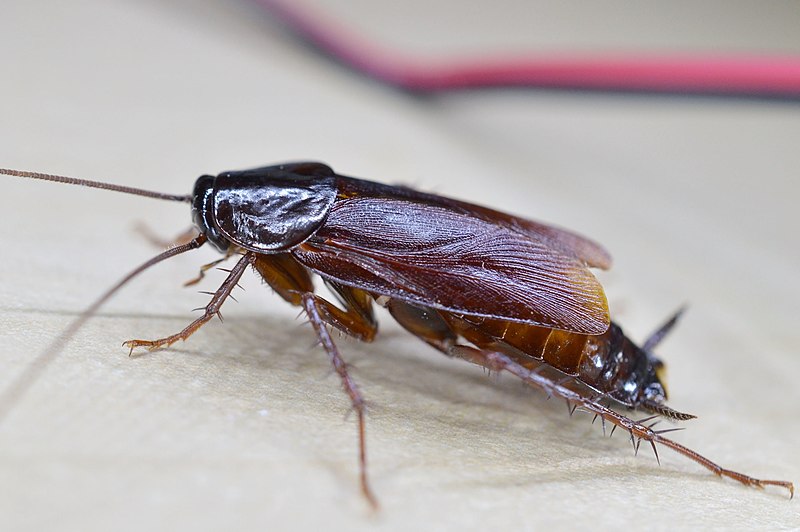

Image by and Credit to: Dimitǎr Boevski
The Oriental Cockroach, sometimes referred to as the black the cockroach, is an enormous black insect that ranges from 0.71″ to 1.14″ (18 – 29 millimeters) long. Adult cockroaches are characterized by an oval-shaped shape and shiny bodies. Even though they have wings these disease-carrying bugs are unable to fly. They are usually found in moist, dark areas and are hard to eliminate.
German Cockroach (Blattella germanica)
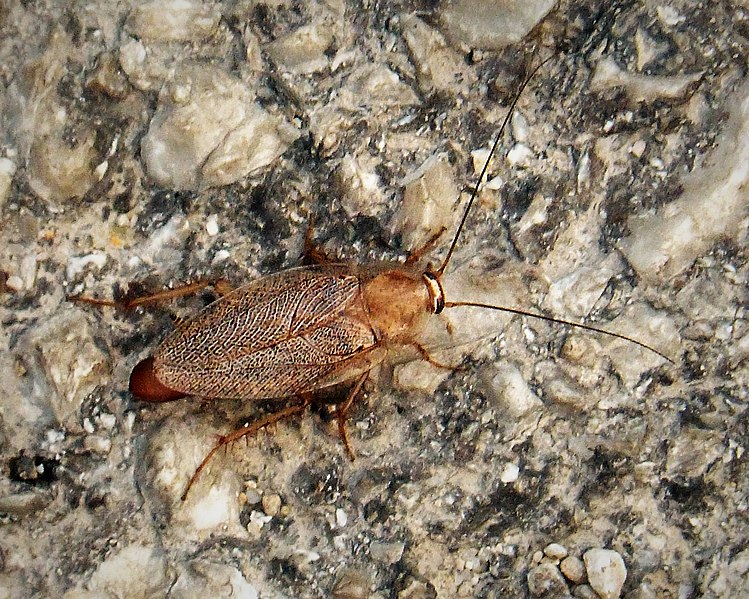

Image by and Credit to: gailhampshire
The most commonly seen small roach that is found in Texas includes that of the German cockroach. Also known as the croton bug The small dark brown to tan bug can grow from 0.43″ to 0.66″ (11-16 millimeters) in length. What distinguishes the brown insect include the parallel stripes that run behind the head, its long antennae, and a small head that is brown. Cockroaches are found both outdoors and inside in Texas.
American Cockroach (Periplaneta americana)
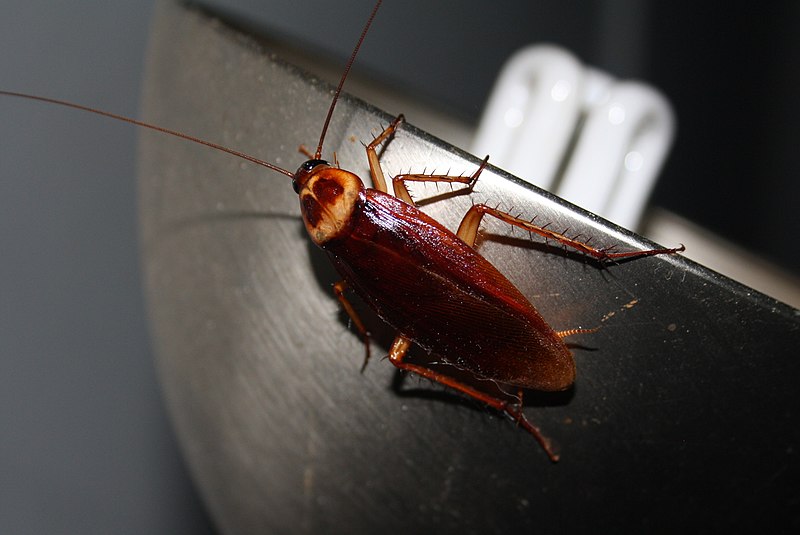

Image by and Credit to: Bob Adams
The American Cockroach is a widespread brown bug that is found in Texas that measures 1.5″ to 2″ (38 -50 millimeters) long. It can be identified by its oval, flat body, incredibly large antennae, and rapid darting movements. The roach with a reddish brown color can travel short distances. It’s among the biggest cockroaches that you can find in Texas.
List of Different Types of Flying Insects in Texas (with Pictures!)
The most peskiest bugs found in Texas include flying bugs that could bite, sting, or even infest the food pantries. Here are a few of the most frequent flying bugs found in Texas.
Gnats (Nematocera)
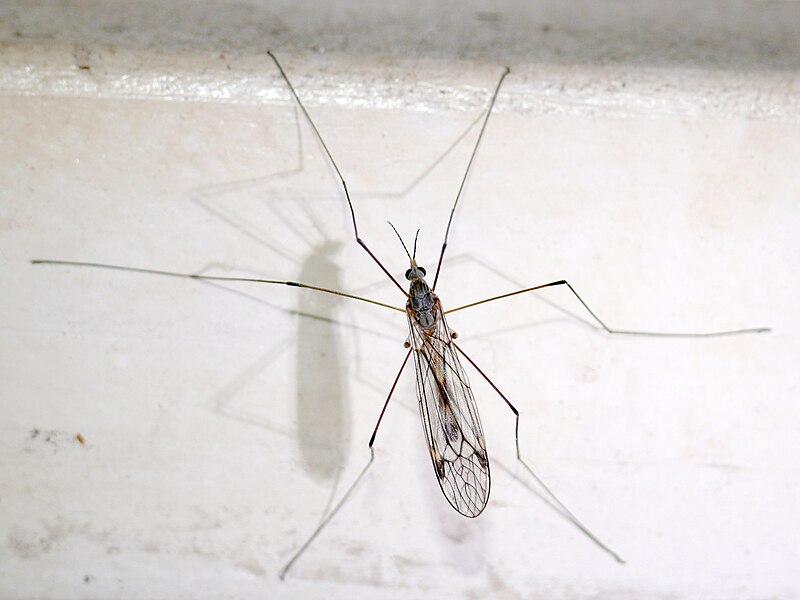

Image by and Credit to: Malte
The fungus Grants (soil grants) are small soil-dwelling black pests of the houseplant which feed on fungi
Texas hosts a variety of species of gnats, small flying insects that have long, thin bodies and slender wings. Certain species of gnats such as eye gnats and buffalo the gnats, may bite and cause itchy, red bumps that appear on your skin. Other species, such as fungus gnats, are usually found in the soil of houseplants, and can be nuisances.
Here are some common kinds of gnats found across Texas:
Eye Gnats:
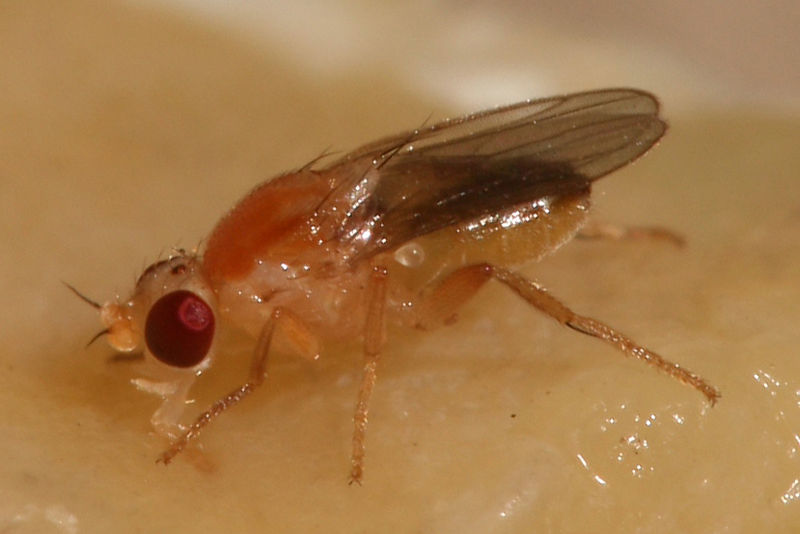

Image by and Credit to: Muhammad Mahdi Karim
Eye gnats, or eye flies, are tiny insects belonging to the Chloropidae family. These minuscule flies measure approximately 0.0625 inch (1.5 mm) in length and are attracted to the moisture around human eyes and other mucous membranes. Eye gnats can cause irritation and discomfort, potentially leading to eye infections if not addressed. Wearing protective eyewear and using screens or repellents in areas prone to eye gnat activity can help prevent these pests from bothering humans and animals.
Fungus Gnats:
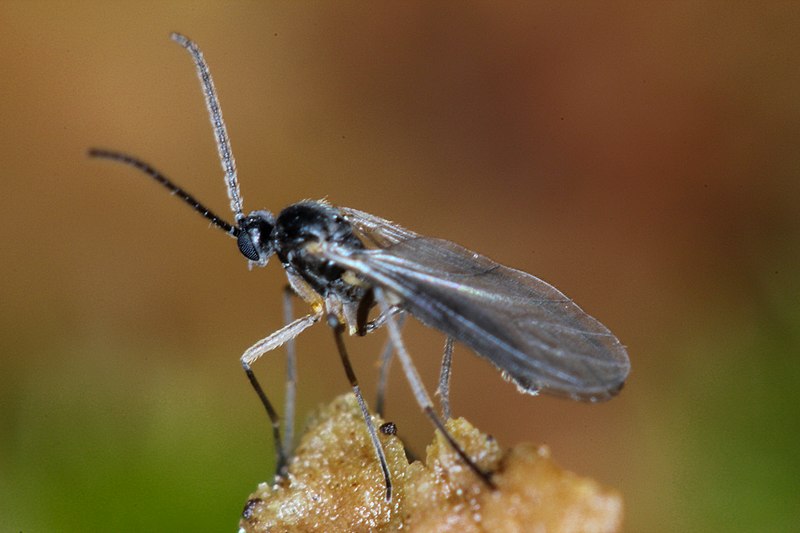

Image by and Credit to: Andy Murray
Fungus gnats are small, delicate insects belonging to the Sciaridae family. Measuring around 0.0625 to 0.125 inches (1.5 to 3 mm) in length, these tiny pests are attracted to decaying organic matter and are commonly found in damp environments, such as overwatered plants and moist soil. Fungus gnats can be a nuisance for indoor plants, as their larvae feed on plant roots. Proper drainage, reducing moisture, and using yellow sticky traps are effective methods to control fungus gnat infestations.
Buffalo Gnats:
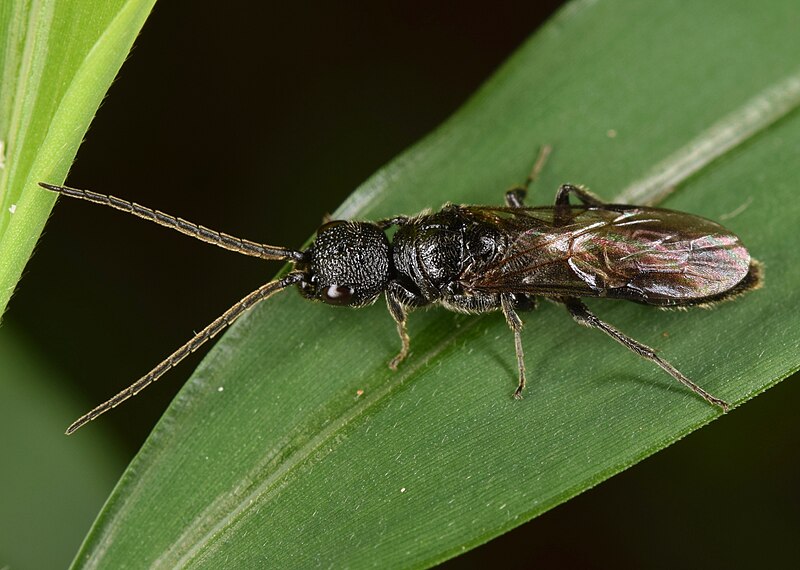

Image by and Credit to: Christina Butler
Buffalo gnats, also known as black flies, are tiny blood-feeding insects belonging to the Simuliidae family. These pests measure between 0.0625 to 0.125 inches (1.5 to 3 mm) in length and are commonly found near fast-flowing streams and rivers. Despite their small size, their bites can be painful and lead to discomfort and allergic reactions. Wearing protective clothing and using insect repellents are essential precautions to avoid buffalo gnat bites during outdoor activities.
Drain Flies (Psychodidae)
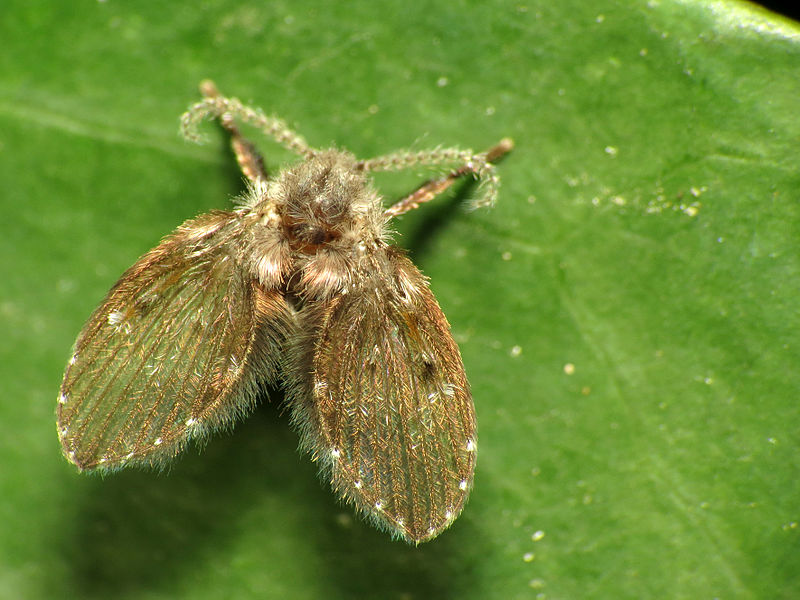

Image by and Credit to: Katja Schulz
Drain flies are tiny, pesky insects that fly around with fuzzy gray bodies and a swaying antennae. Adult furry moth-like insects measure 0.12″ (3.1 millimeters) and can be seen in close proximity to drains, sewage systems and other damp places. Their larvae are found in slimy sludge that drains that are located in kitchen and bathroom sinks.
Drain flies can also be referred to as sewer Flies, sewer gnats, filter flies, and sink flies. The removal of these annoying fly is a challenge because larvae are aquatic and reside in drains. Try pouring boiling water down your drains in order to eliminate the larvae.
For a quick and easy way to clean your drain mix half 1 cup of salt and half a cup baking soda, and then pour it down the drain. After that, add one Cup of white vinegar. Let it sit overnight, then wash with hot water the next morning to kill any fly eggs and larvae.
Texas Flying ID of the insect Drain flies can be annoying moth-like insects that have grey, fuzzy appearance and antennae that are segmented, which is common in the vicinity of sinks and drains.
Fruit Flies (Drosophila melanogaster)
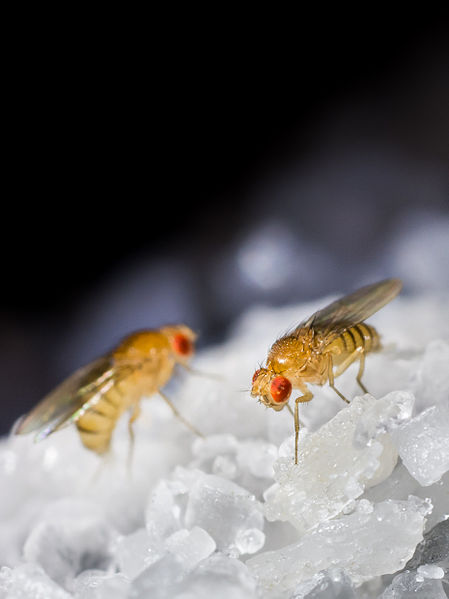

Image by and Credit to: Francisco Romero Ferrero
Flies that eat fruit are small insects with light or tan brown bodies, eyes with red tiny wings that are translucent, and black bands that run across their abdomens. Small fruit flies are 0.10″ (2.5 millimeters) in length. Small brown flies are prevalent in Texas homes in the summer months and hover over ripe or decaying fruit.
Fruit flies don’t pose a threat and do not spread diseases. However, an infestation in your home could be a nuisance. Keep vegetables and fruits in the refrigerator or in airtight containers to eliminate the flying insects. Also, throw away fruits that are rotting or too ripe in the trash can outside and ensure that kitchen surfaces are clean.
How to Identify: Fruit flies can be identifiable because of their small size, lighter brown body and their red eyes. They are often found in fruit and can cause nuisance in kitchens and stores.
Indian Meal Moth (Pantry Moths) (Plodia interpunctella)
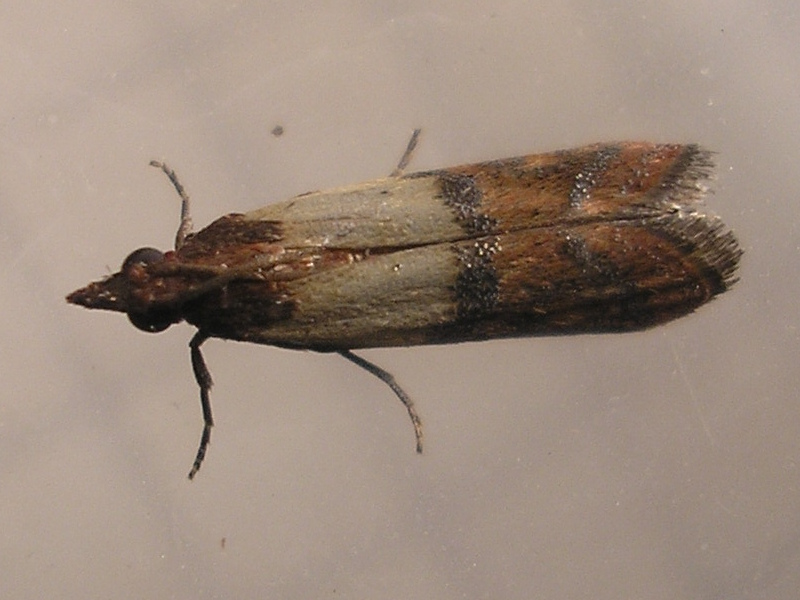

Image by and Credit to: Pudding4brains
The Indian meal moth can be described as a typical pantry bug, with two-toned gray and beige with black wings. The tiny moth, which is gray and brown, measures 0.39″ (10 mm) with a wingspan of 0.6″ to 0.79″ (16 – 20 millimeters). Indian meal moths are small and are usually found infesting stored cereals, grains, pasta, rice and even flour.
There are many Indian meal moths fluttering around through kitchens, storage cabinets and in pantries. Food items that are infested by larvae may show silky web-like strands that look like food packaging, skins made of cast or pepper-like spots (feces).
How to Identify: Identification features of the Indian meal moth include its distinctive cream-gray forewings, with coppery-brown wingtips, and gray hindwings.
Horse Flies (Tabanidae)
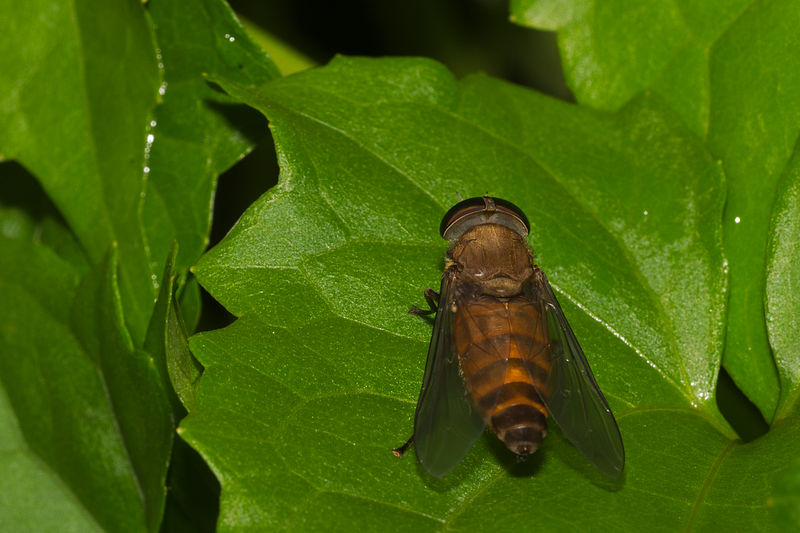

Image by and Credit to: Jeevan Jose
Horse flies are huge sturdy flies, well-known for their bites that can be painful. They are prevalent in Texas and are distinguished through their black or dark brown coloring as well as their large compound eyes and strong bodies with long antennae. The large fliers are 0.20″ and 1″ (5 to 25 millimeters) long.
Horse flies are usually located near water bodies or in areas of rurality where livestock are. Female horse flies can deliver painstaking bites as they search for blood meal. The bites can cause itching, swelling and pain. Horse flies have been known to bite both animals and humans such as cattle, horses and deer.
How to Identify: Horses flying in Texas may differ in the appearance as well as species. Many species are iridescent, or metallic colors. They are up to 1″ (25 millimeters) in length.
Mosquitoes (Culicidae)
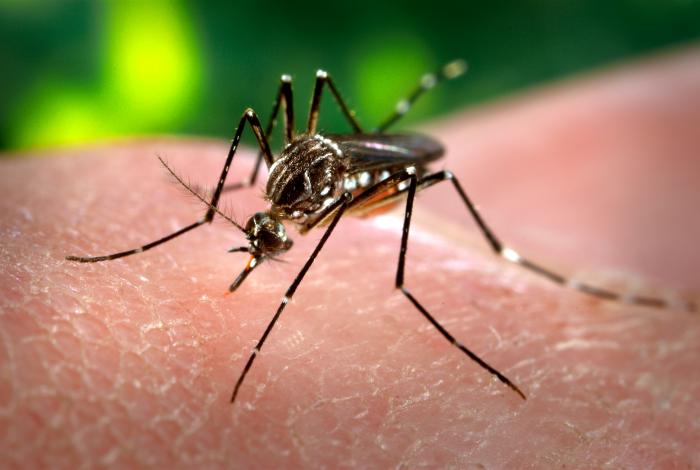

Image by and Credit to: James Gathany
There are a variety of mosquito species that are flying pests, and are common across all of the Lone Star State. The bite-sucking bugs have slim bodies, long legs and mouthparts with long proboscis. The tiny flying insects can get in size to 0.39″ (10 millimeters) in length. Female mosquitoes eat blood from animals and humans while males feast on nectar of plants.
The most frequent kinds of mosquitoes that are found in Texas include Aedes, Culex, and Anopheles. For instance Culex, the Asian Tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) is prevalent throughout the south. It’s easily identified by its black fly bug that has white stripes along its legs as well as the aggressive bites.
How to Identify: Mosquitoes are distinguished by their tiny size, long proboscis that is for sucking blood, as well as the buzzing sound near your ear.
Bonus: Other Types of Texas ‘Bugs’
A variety of other smaller creatures that live in Texas are known as bugs, even though they’re not considered to be bugs or insects in the strict sense.
Spiders
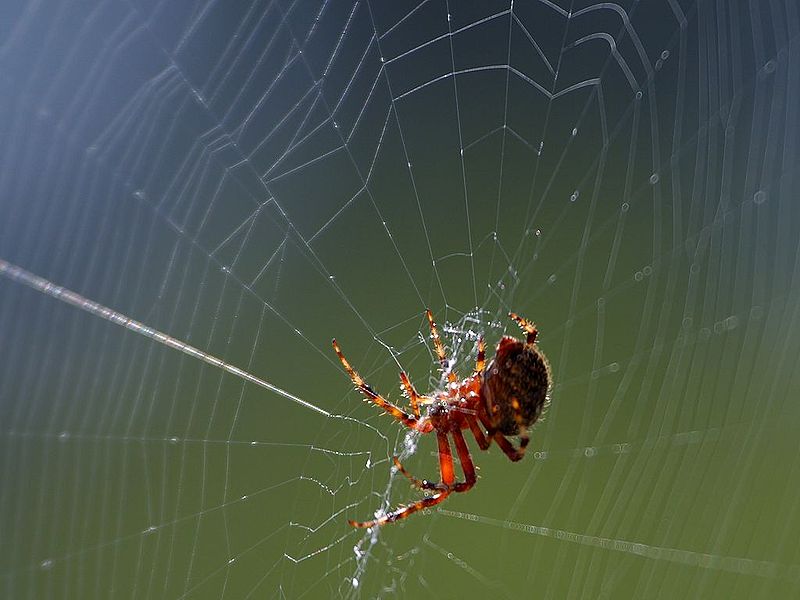

Image by and Credit to: Jon Sullivan
Spiders aren’t insects, however, many call them bugs due to their irritation. They are arachnids. They can be distinguished through their 8 legs and two body segments and the absence of antennae. Additionally, they have several eyes as well as huge mandibles that they use to bite their prey. The most common spider species in Texas include:
Woodlouse Spider (Dysdera crocata)
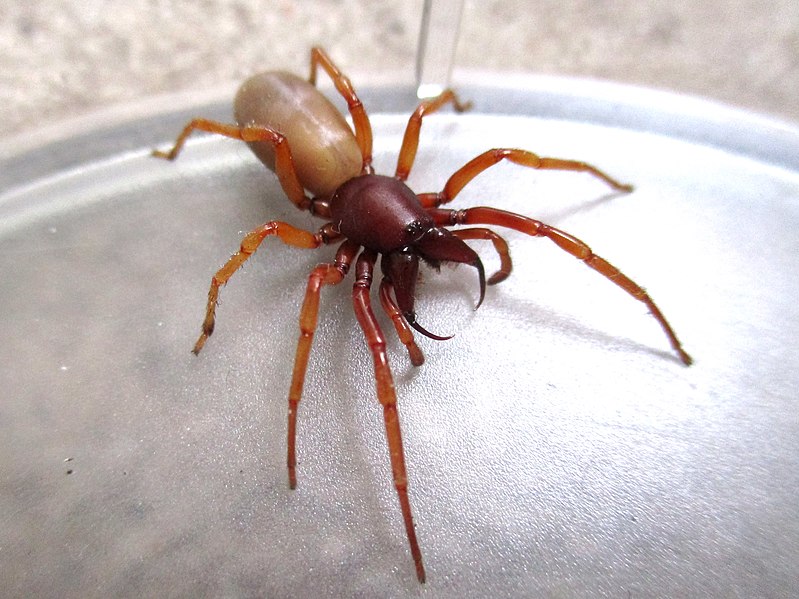

Image by and Credit to: Dat doris
The woodlouse spider, Dysdera crocata, is a ground-dwelling spider species known for its specialized fangs designed for hunting woodlice and other prey. These spiders are harmless to humans and play a vital role in managing woodlice populations in gardens and outdoor areas. Woodlouse spiders are identifiable by their reddish-brown color and long, slender legs.
Woodlouse Hunter Spider (Dysderidae)
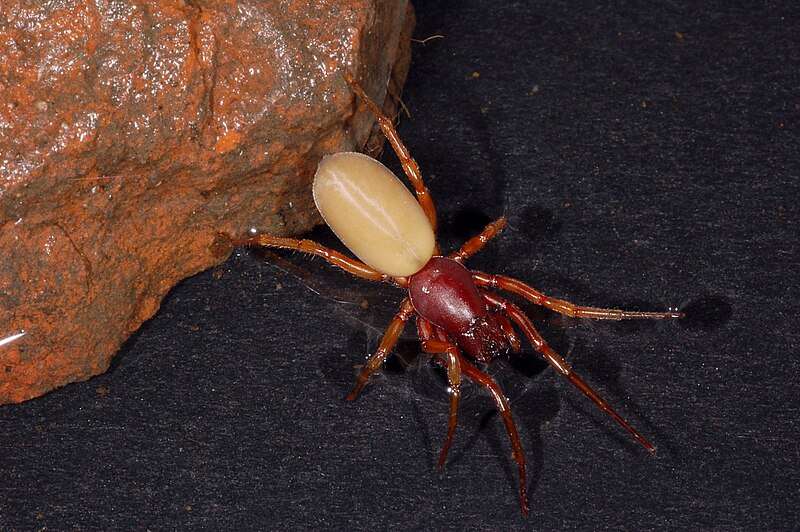

Image by and Credit to: Fritz Geller-Grimm
Woodlouse hunter spiders, belonging to the Dysderidae family, are nocturnal hunters that prey on woodlice, insects, and other small arthropods. These spiders do not pose a threat to humans and are valuable for controlling woodlice populations. Woodlouse hunter spiders are typically found in damp environments like gardens and basements.
White-banded Crab Spider (Misumenoides formosipes)
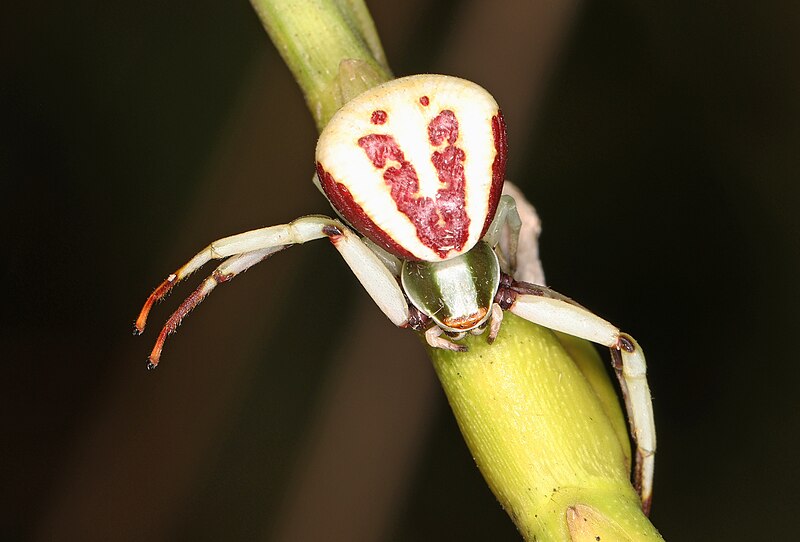

Image by and Credit to: Judy Gallagher
The white-banded crab spider, Misumenoides formosipes, is a crab spider species known for its ability to change color to match its surroundings. These spiders wait patiently on flowers, blending in until unsuspecting prey comes within reach. Their excellent camouflage makes them effective hunters in gardens and flowerbeds.
Crab Spiders (Thomisidae)
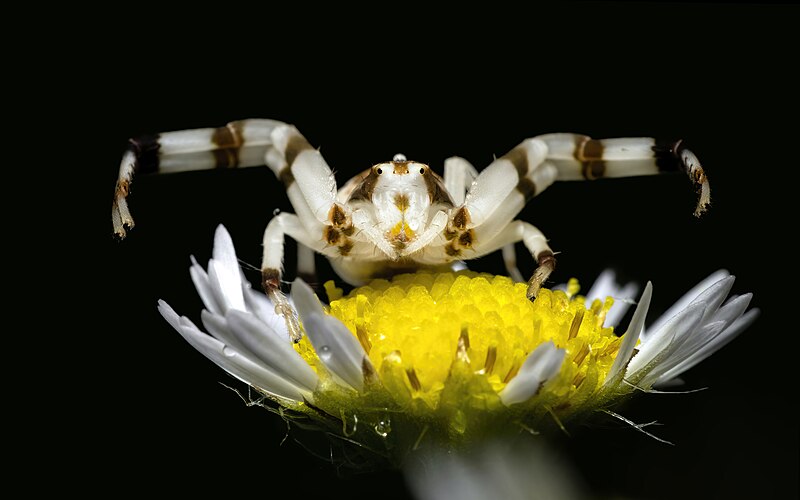

Image by and Credit to: Prasan Shrestha
Crab spiders, belonging to the Thomisidae family, are named for their crab-like appearance and sideways movement. These spiders are skilled hunters and do not build webs to catch prey. Crab spiders come in various colors, often matching the flowers they inhabit. They are beneficial in gardens, preying on insects and helping with natural pest control.
Common House Spider (Parasteatoda tepidariorum)
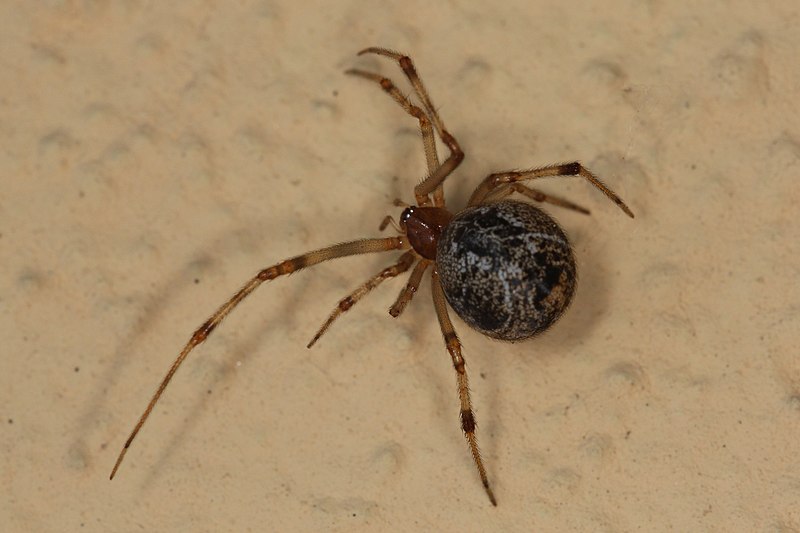

Image by and Credit to: Holger Krisp
The common house spider, Parasteatoda tepidariorum, is a small spider species often found indoors, weaving messy cobwebs in corners and crevices. Although they may startle homeowners, these spiders are harmless and play a role in controlling insect populations. Regular cleaning and removing webs can keep their presence minimal inside homes.
Long-bodied Cellar Spider (Pholcus phalangioides)
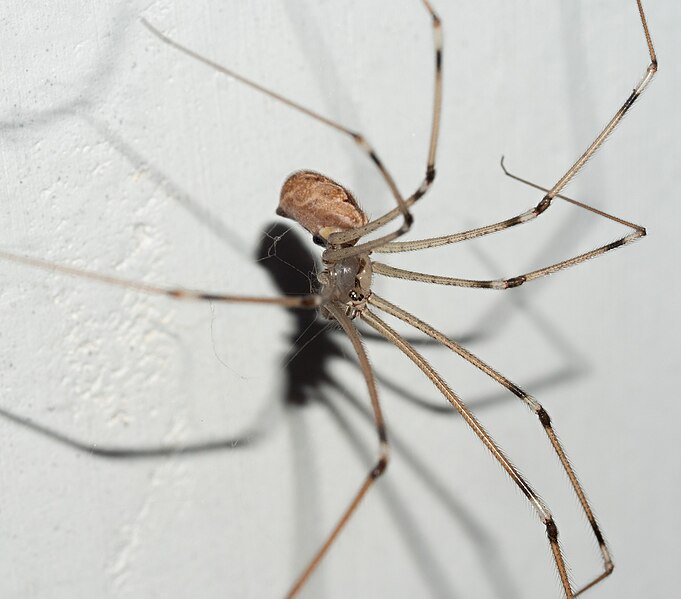

Image by and Credit to: Luis Fernández García
Long-bodied cellar spiders, Pholcus phalangioides, are delicate spiders commonly found in damp, dark environments like cellars and basements. They have long, thin legs and build irregular webs. Despite their creepy appearance, these spiders are harmless to humans and help control other pests by capturing and feeding on insects like mosquitoes and flies.
Brown Recluse Spider (Loxosceles reclusa)
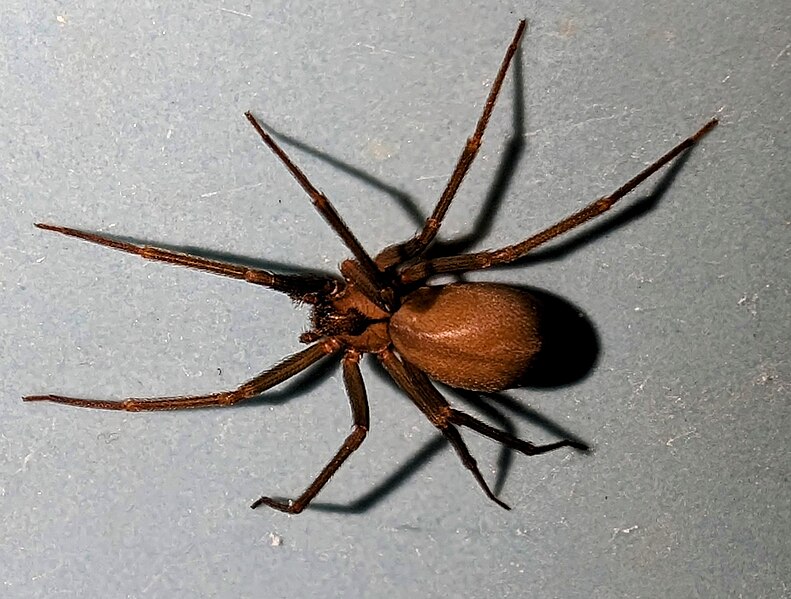

Image by and Credit to: Conway Hawn
Brown recluse spiders, scientifically known as Loxosceles reclusa, are venomous spiders with a violin-shaped mark on their back. These spiders prefer quiet, undisturbed areas and can be found in dark corners, closets, and attics. Their bites can cause necrotic skin lesions and, in severe cases, systemic reactions. Regular cleaning, sealing cracks, and reducing clutter are effective ways to minimize the risk of brown recluse spider encounters inside homes.
Black Widow Spider (Latrodectus mactans)
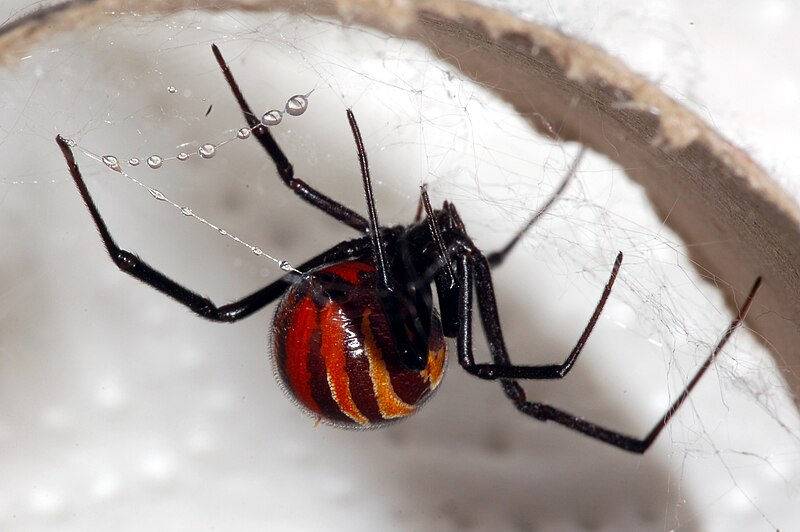

Image by and Credit to: Fritz Geller-Grimm
The black widow spider, Latrodectus mactans, is a venomous arachnid known for its distinctive black color and red hourglass-shaped mark on its abdomen. Found in dark, secluded areas, these spiders possess potent venom that can cause severe reactions in humans. Black widow bites may lead to muscle pain, nausea, and in rare cases, paralysis. Identifying and avoiding their habitats, such as woodpiles and sheds, is essential to prevent encounters with these dangerous spiders.
Millipedes
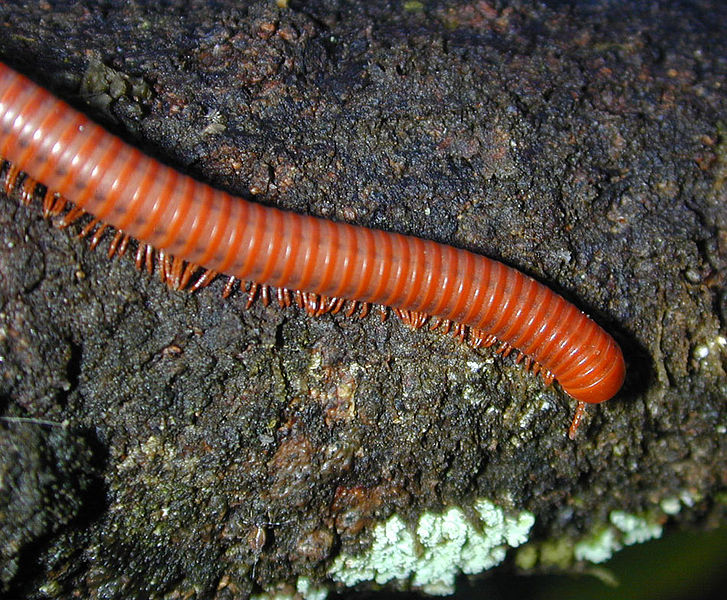

Image by and Credit to: Eric Guinther
Millipedes are arthropods of cylindrical shape with two pairs of legs for each segment. These worm-like creatures range from 0.08″ to 14″ (2 – 350 mm) by length based upon the type of animal. They’re typically black or dark brown. They are usually found in damp areas like in leaf litter, or decaying logs.
Millipedes aren’t harmful to humans, and they don’t bite. Certain species may release a chemical defense which can cause skin irritations and allergic reactions in people who are sensitive.
How to Identify: Millipedes are black or dark brown arthropods resembling worms that have a segmented body with two legs per segment, separating these from centipedes.
Biting Mites
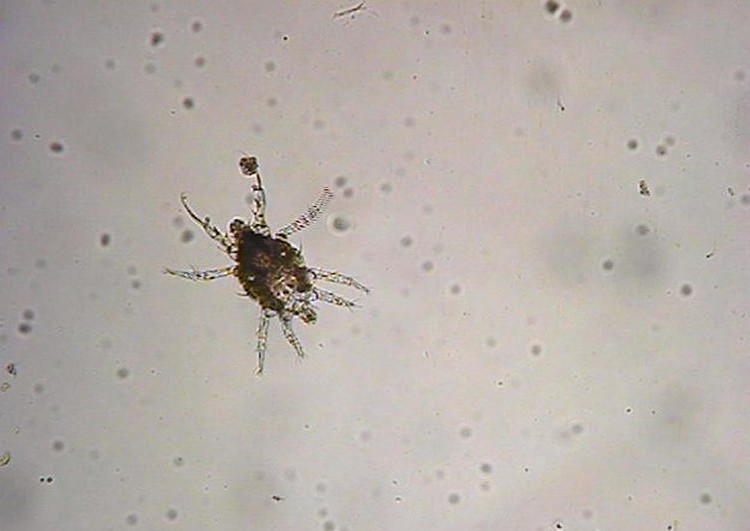

Image by and Credit to: Chazz Hesselein
Biting mites are small Arachnids which can cause irritation and discomfort when they sting humans or other animals. These mites aren’t apparent for the untrained eye, and require magnification in order to be observed. Mites that are found in your home may be an indication of an infestation of vermin. Their bites can trigger itching, irritation, or tiny bumps that appear over the body.
Pillbugs (Armadillidium vulgare)
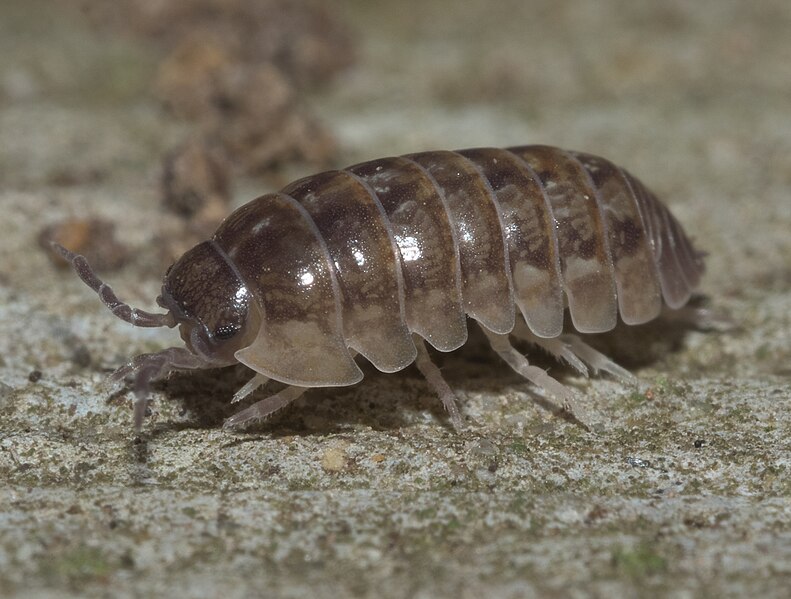

Image by and Credit to: xpda
Pillbugs, also referred to as woodlice or roly-polies are tiny crustaceans that have armored bodies that measure approximately 0.70 inches (18 millimeters) long. The bugs that are easily recognized have oval-shaped bodies that are segmented and have seven legs. Their most distinctive characteristic is the ability to transform into the shape of a ball when they’re threatened. Pillbugs can be found in the fallen foliage, stones and in mulch.
Pillbugs range from 0.25″ to 0.5″ (6 12-12 millimeters) in length. The grayish bugs prefer dark areas and feed on plants that are dying and decaying organic matter. They are also small pests in gardens, where the gray bugs consume plant roots and leaves.
Sometimes, they can be an issue in the house, and they are known to breed in dark, damp places. They do not cause harm and can only be a nuisance.
How to Identify: Pillbugs are identified by their oval-shaped shape, dark body with a segmented look and their ability to form an elongated ball.
Striped Bark Scorpion (Centruroides vittatus)
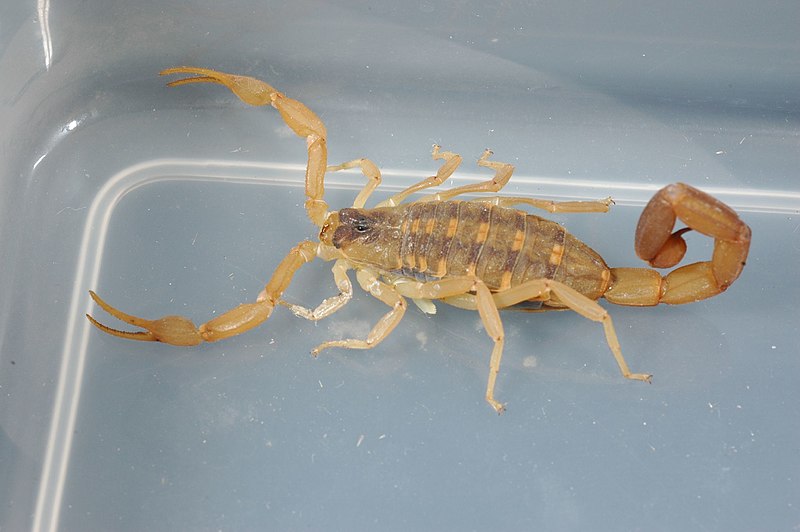

Image by and Credit to: Clinton & Charles Robertson
The scorpion with striped stripes is an arthropod of pale yellow with two dark, longitudinal stripes running across its back. The yellowish scorpion is typically found in the dry and desert regions of Texas and is 2.5 up to three inches (63 – 76 millimeters) long. They can enter homes and can deliver an unpleasant sting.
How to Identify: The small native scorpion can be identified by dark stripes across its pale yellow or orange body as well as a triangular marking near its head.
Texas Redheaded Centipede (Scolopendra heros)
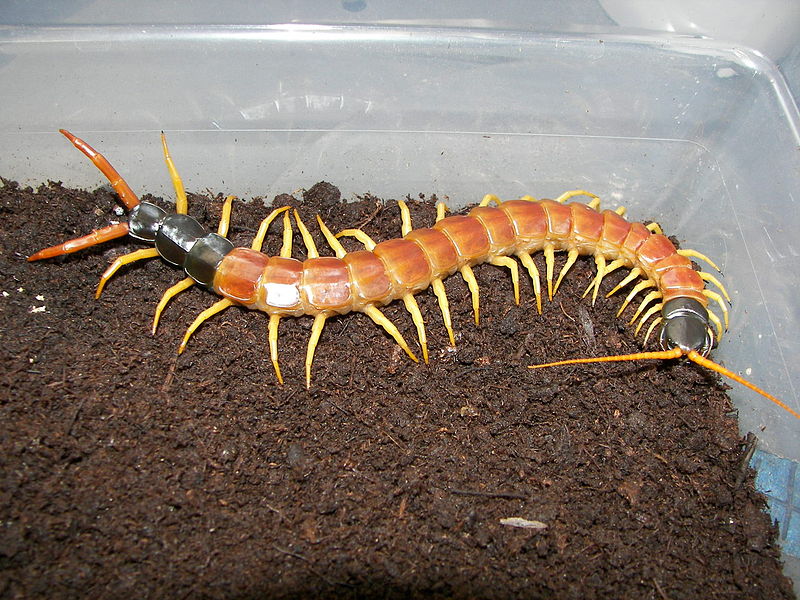

Image by and Credit to: John
It is the Texas red-headed centipede a massive arthropod with a long, greenish-black body, an edgy head that is dark reddish and orange, as well as light orange legs. The big centipede can grow up to 6.5″ (170 millimeters) and sometimes, even larger. The venomous beast can sting humans and cause the skin to red, swelling and extreme pain.
How to Identify: To identify the Texas redheaded centipede look for its dark-black-green physique, its red-colored head and numerous orange legs.
Lone Star Tick (Amblyomma americanum)
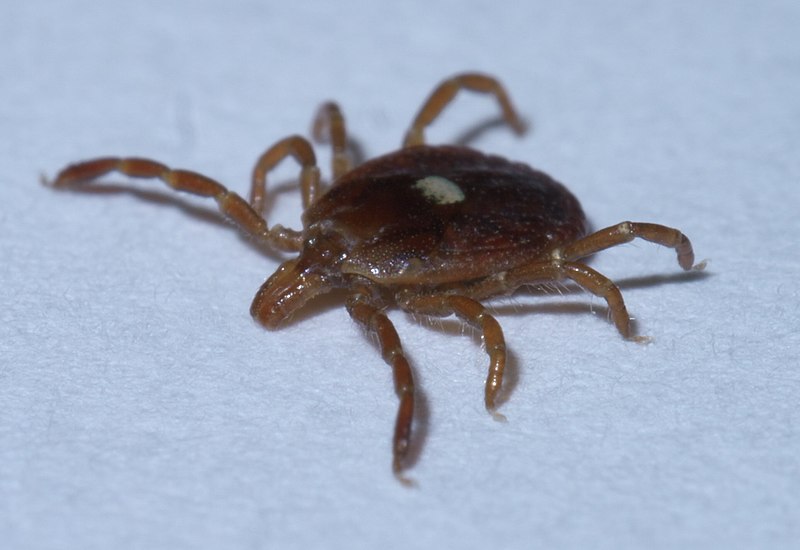

Image by and Credit to: xpda
The Lone Star tick is a popular tick species found throughout Texas.
The ticks are reddish brown with oval-shaped bodies. They also have a an enticing silvery-white spot on females’ backs. Male ticks are white with lines around the edges on their rears. They measure 0.33″ (8.4 millimeters) in length. As with many tick species found in Texas They pierce the skin to consume blood-feeding. Additionally they transmit diseases like Lyme disease.
Other tick species found in Texas are:
American Dog Ticks (Dermacentor variabilis):
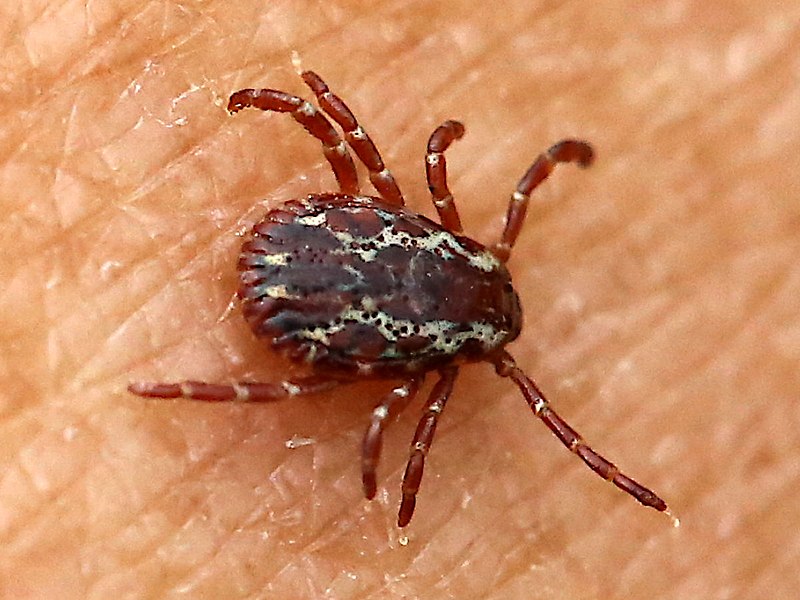

Image by and Credit to: Peterwchen
American dog ticks, Dermacentor variabilis, are ectoparasites measuring approximately 0.118 inches (3 mm) in length. These ticks infest dogs, humans, and other animals, serving as carriers of diseases such as Rocky Mountain spotted fever and tularemia. Dermacentor variabilis ticks are identifiable by their reddish-brown color and are commonly found in areas with tall grasses and shrubs. Regular tick checks, tick prevention products, and immediate tick removal are crucial to prevent tick-borne illnesses.
Ticks of Deer (Ixodes Capularis):
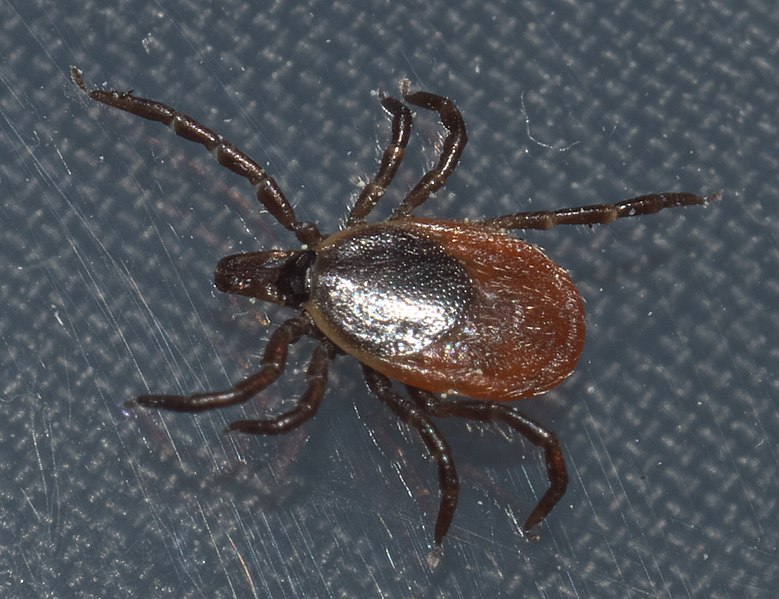

Image by and Credit to: xpda
Ticks of deer, scientifically known as Ixodes Capularis, are parasitic arachnids measuring between 0.039 to 0.059 inches (1 to 1.5 mm) in length. These ticks infest deer and other wildlife, posing a threat to humans and pets. Ixodes Capularis ticks are vectors for various diseases, including Lyme disease and anaplasmosis. Precautions such as wearing protective clothing and using tick repellents are essential to prevent tick bites and associated illnesses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, navigating the world of Texas insects and bugs is made easier with this comprehensive guide.
Whether it’s identifying annoying pests or genuine bugs, understanding their characteristics and habitats is key to managing them effectively. By learning about these creatures, their behaviors, and ecological roles, you’re equipped to coexist harmoniously with Texas’s diverse insect population. Remember, knowledge is your best tool in maintaining a balanced ecosystem.
Here’s to a bug-friendly understanding and a pest-free environment in the Lone Star State!
Featured and Pinterest images credit to: John


